Neural correlates of the automatic processing of threat facial signals
- PMID: 12843265
- PMCID: PMC6741280
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05627.2003
Neural correlates of the automatic processing of threat facial signals
Abstract
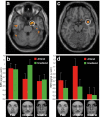
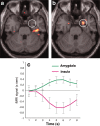
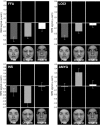
The present study examined whether automaticity, defined here as independence from attentional modulation, is a fundamental principle of the neural systems specialized for processing social signals of environmental threat. Attention was focused on either scenes or faces presented in a single overlapping display. Facial expressions were neutral, fearful, or disgusted. Amygdala responses to facial expressions of fear, a signifier of potential physical attack, were not reduced with reduced attention to faces. In contrast, anterior insular responses to facial expressions of disgust, a signifier of potential physical contamination, were reduced with reduced attention. However, reduced attention enhanced the amygdala response to disgust expressions; this enhanced amygdala response to disgust correlated with the magnitude of attentional reduction in the anterior insular response to disgust. These results suggest that automaticity is not fundamental to the processing of all facial signals of threat, but is unique to amygdala processing of fear. Furthermore, amygdala processing of fear was not entirely automatic, coming at the expense of specificity of response. Amygdala processing is thus specific to fear only during attended processing, when cortical processing is undiminished, and more broadly tuned to threat during unattended processing, when cortical processing is diminished.
Figures
References
-
- Adolphs R, Tranel D, Damasio H, Damasio A ( 1994) Impaired recognition of emotion in facial expressions following bilateral damage to the human amygdala. Nature 372: 669–672. - PubMed
-
- Anderson AK, Phelps EA ( 2001) Lesions of the human amygdala impair enhanced perception of emotionally salient events. Nature 411: 305–309. - PubMed
-
- Birbaumer N, Grodd W, Diedrich O, Klose U, Erb M, Lotze M, Schneider F, Weiss U, Flor H ( 1998) fMRI reveals amygdala activation to human faces in social phobics. NeuroReport 9: 1223–1226. - PubMed
-
- Breiter HC, Etcoff NL, Whalen PJ, Kennedy WA, Rauch SL, Buckner RL, Strauss MM, Hyman SE, Rosen BR ( 1996) Response and habituation of the human amygdala during visual processing of facial expression. Neuron 17: 875–887. - PubMed
-
- Cahill L, Haier RJ, White NS, Fallon J, Kilpatrick L, Lawrence C, Potkin SG, Alkire MT ( 2001) Sex-related difference in amygdala activity during emotionally influenced memory storage. Neurobiol Learn Mem 75: 1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
