Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediates activity-dependent dendritic growth in nonpyramidal neocortical interneurons in developing organotypic cultures
- PMID: 12843269
- PMCID: PMC6741232
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05662.2003
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediates activity-dependent dendritic growth in nonpyramidal neocortical interneurons in developing organotypic cultures
Abstract
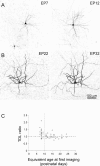
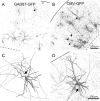
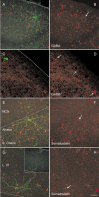
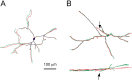
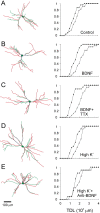
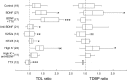
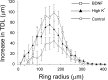
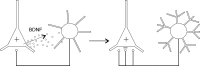
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes postnatal maturation of GABAergic inhibition in the cerebral and cerebellar cortices, and its expression and release are enhanced by neuronal activity, suggesting that it acts in a feedback manner to maintain a balance between excitation and inhibition during development. BDNF promotes differentiation of cerebellar, hippocampal, and neostriatal inhibitory neurons, but its effects on the dendritic development of neocortical inhibitory interneurons remain unknown. Here, we show that BDNF mediates depolarization-induced dendritic growth and branching in neocortical interneurons. To visualize inhibitory interneurons, we biolistically transfected organotypic cortical slice cultures from neonatal mice with green fluorescent protein (GFP) driven by the glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)67 promoter. Nearly all GAD67-GFP-expressing neurons were nonpyramidal, many contained GABA, and some expressed markers of neurochemically defined GABAergic subtypes, indicating that GAD67-GFP-expressing neurons were GABAergic. We traced dendritic trees from confocal images of the same GAD67-GFP-expressing neurons before and after a 5 d growth period, and quantified the change in total dendritic length (TDL) and total dendritic branch points (TDBPs) for each neuron. GAD67-GFP-expressing neurons growing in control medium exhibited a 20% increase in TDL, but in 200 ng/ml BDNF or 10 mm KCl, this increase nearly doubled and was accompanied by a significant increase in TDBPs. Blocking action potentials with TTX did not prevent the BDNF-induced growth, but antibodies against BDNF blocked the growth-promoting effect of KCl. We conclude that BDNF, released by neocortical pyramidal neurons in response to depolarization, enhances dendritic growth and branching in nearby inhibitory interneurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vertical bias in dendritic trees of non-pyramidal neocortical neurons expressing GAD67-GFP in vitro.Cereb Cortex. 2001 Jul;11(7):666-78. doi: 10.1093/cercor/11.7.666. Cereb Cortex. 2001. PMID: 11415968
-
Neuronal activity and brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulate the density of inhibitory synapses in organotypic slice cultures of postnatal hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2000 Nov 1;20(21):8087-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-21-08087.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11050130 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor acutely depresses excitatory synaptic transmission to GABAergic neurons in visual cortical slices.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Aug;20(3):709-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03523.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15255981
-
Neurotrophins and activity-dependent plasticity of cortical interneurons.Trends Neurosci. 1997 May;20(5):198-202. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(96)01026-0. Trends Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9141194 Review.
-
Neocortical inhibitory system.Folia Biol (Praha). 2009;55(6):201-17. Folia Biol (Praha). 2009. PMID: 20163769 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuregulins 1, 2, and 3 Promote Early Neurite Outgrowth in ErbB4-Expressing Cortical GABAergic Interneurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Aug;57(8):3568-3588. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-01966-7. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32542595
-
LIS1-dependent retrograde translocation of excitatory synapses in developing interneuron dendrites.Nat Commun. 2012 Mar 6;3:722. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1736. Nat Commun. 2012. PMID: 22395613 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of BDNF in Age-Dependent Changes of Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Markers in the Human Prefrontal Cortex.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Dec;41(13):3080-3091. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.126. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27417517 Free PMC article.
-
What is the biological significance of BDNF mRNA targeting in the dendrites? Clues from epilepsy and cortical development.Mol Neurobiol. 2006 Feb;33(1):17-32. doi: 10.1385/MN:33:1:017. Mol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16388108 Review.
-
BDNF Therapeutic Mechanisms in Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 29;23(15):8417. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158417. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955546 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agmon A, O'Dowd DK ( 1992) NMDA receptor-mediated currents are prominent in the thalamocortical synaptic response before maturation of inhibition. J Neurophysiol 68: 345–349. - PubMed
-
- Aguado F, Carmona MA, Pozas E, Aguilo A, Martinez-Guijarro FJ, Alcantara S, Borrell V, Yuste R, Ibanez CF, Soriano E ( 2003) BDNF regulates spontaneous correlated activity at early developmental stages by increasing synaptogenesis and expression of the K+/Cl – co-transporter KCC2. Development 130: 1267–1280. - PubMed
-
- Alcantara S, Ferrer I, Soriano E ( 1993) Postnatal development of parvalbumin and calbindin D28K immunoreactivities in the cerebral cortex of the rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 188: 63–73. - PubMed
-
- Altar CA, Cai N, Bliven T, Juhasz M, Conner JM, Acheson AL, Lindsay RM, Wiegand SJ ( 1997) Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain. Nature 389: 856–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
