Brain-derived neurotrophic factor inhibits human immunodeficiency virus-1/gp120-mediated cerebellar granule cell death by preventing gp120 internalization
- PMID: 12843275
- PMCID: PMC6741234
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05715.2003
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor inhibits human immunodeficiency virus-1/gp120-mediated cerebellar granule cell death by preventing gp120 internalization
Abstract
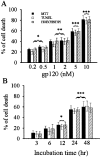
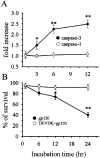
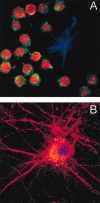
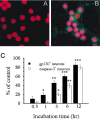
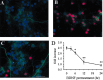
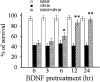
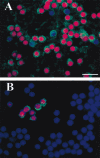
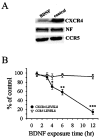
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope protein gp120 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of HIV-1 dementia. Thus, inhibition of gp120 activity could reduce HIV toxicity in the brain. We have used primary cultures of rat cerebellar granule cells to examine mechanisms whereby gp120 causes cell death and to characterize neuroprotective agents. gp120 induced a time- and concentration-dependent apoptotic cell death, which was caspase-3-mediated but caspase-1 independent, and was totally blocked by the irreversible caspase-3-like protease inhibitor N-acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-chloromethylketone. Caspase-3 activation was observed only in neurons that internalize gp120, indicating that internalization is key to gp120 toxicity. Because brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) prevents caspase-3-mediated neuronal cell death, we examined whether BDNF could prevent gp120-mediated apoptosis. Preincubation of neurons with BDNF before the addition of gp120 reduced caspase-3 activation, and consequently rescued 80% of neurons from apoptosis. Most importantly, BDNF reduced the levels of CXC chemokine receptor-4 (CXCR4), a receptor that mediates HIV-1 gp120-induced apoptosis. This effect correlated with the ability of BDNF to reduce gp120 internalization and apoptosis. Moreover, BDNF blocked the neurotoxic effect of stromal-derived factor-1alpha, a natural ligand for CXCR4, further establishing a correlation between neuroprotection and downregulation of CXCR4. We propose that BDNF may be a valid therapy to slow down the progression of HIV/gp120-mediated neurotoxicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 and not the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor mediates gp120 neurotoxicity in cerebellar granule cells.J Neurosci Res. 2004 Jan 1;75(1):75-82. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10826. J Neurosci Res. 2004. PMID: 14689450
-
Semisynthetic sphingoglycolipid LIGA20 is neuroprotective against human immunodeficiency virus-gp120-mediated apoptosis.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Apr;83(5):890-6. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20780. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16477610
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is neuroprotective against human immunodeficiency virus-1 envelope proteins.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Aug;1053:247-57. doi: 10.1196/annals.1344.022. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16179530
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB protects neurons from HIV-1/gp120-induced cell death.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2004;16(1-2):51-7. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v16.i12.50. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15581399 Review.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor prevents human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protein gp120 neurotoxicity in the rat nigrostriatal system.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Dec;1122:144-54. doi: 10.1196/annals.1403.010. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18077570 Review.
Cited by
-
Clonal immortalized human glial cell lines support varying levels of JC virus infection due to differences in cellular gene expression.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;8(5):1303-19. doi: 10.1007/s11481-013-9499-8. Epub 2013 Sep 20. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24052414
-
HIV-associated synaptic degeneration.Mol Brain. 2017 Aug 29;10(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13041-017-0321-z. Mol Brain. 2017. PMID: 28851400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus gp120-induced apoptosis of human neuroblastoma cells in the absence of CXCR4 internalization.J Neurovirol. 2006 Jun;12(3):211-8. doi: 10.1080/13550280600848373. J Neurovirol. 2006. PMID: 16877302 Free PMC article.
-
Essential involvement of the NMDA receptor in ethanol preconditioning-dependent neuroprotection from amyloid-betain vitro.J Neurochem. 2009 Oct;111(2):580-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06351.x. Epub 2009 Aug 19. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19694907 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-associated depression: contributions of immuno-inflammatory, monoaminergic, neurodegenerative, and neurotrophic pathways.J Neurovirol. 2013 Aug;19(4):314-27. doi: 10.1007/s13365-013-0177-7. Epub 2013 Jul 19. J Neurovirol. 2013. PMID: 23868513 Review.
References
-
- Bachis A, DeBernardi MA, Mocchetti I ( 2000) Brain derived neurotrophic factor protects cerebellar granule cells against gp120-mediated cell death. Soc Neurosci Abstr 26: 89.8.
-
- Bachis A, Rabin SJ, Del Fiacco M, Mocchetti I ( 2002) Gangliosides prevent excitotoxicity through activation of TrkB receptor. Neurotox Res 3: 225–234. - PubMed
-
- Bagetta G, Corasaniti MT, Aloe L, Berliocchi L, Costa N, Finazzi-Agro A, Nistico G ( 1996) Intracerebral injection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 coat protein gp120 differentially affects the expression of nerve growth factor and nitric oxide synthase in the hippocampus of rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 928–933. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
