The trophic role of oligodendrocytes in the basal forebrain
- PMID: 12843289
- PMCID: PMC6741226
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05846.2003
The trophic role of oligodendrocytes in the basal forebrain
Abstract
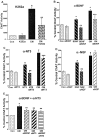
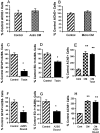
Traditionally, the primary function of oligodendrocytes (OLGs) in the CNS has been considered to be myelination. Here, we investigated whether OLGs may play a trophic role, particularly during development. Neurotrophin expression was assessed in postnatal day 7 basal forebrain (BF) OLGs, using in situ hybridization and detection of myelin basic protein. Nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) mRNAs were revealed in OLGs in vivo and in culture. To determine whether OLGs support nearby neurons, we examined the influence of OLGs on BF cholinergic neurons. Neuronal function was enhanced by cocultured OLGs and OLG conditioned medium. Moreover, trophic effects of OLG conditioned medium were partially blocked by K252a, a trk tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and by neutralizing anti-BDNF or anti-NT-3 antisera, indicating that neurotrophins may mediate these effects, perhaps in concert with other signals. Our studies support a novel role for OLGs in providing local trophic support for neurons in the CNS.
Figures

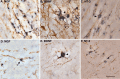
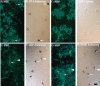
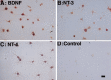
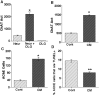
References
-
- Abiru Y, Katoh-Semba R, Nishio C, Hatanaka H ( 1998) High potassium enhances secretion of neurotrophic factors from cultured astrocytes. Brain Res 809: 115-126. - PubMed
-
- Alderson RF, Alterman AL, Barde YA, Lindsay RM ( 1990) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases survival and differentiated functions of rat septal cholinergic neurons in culture. Neuron 5: 297-306. - PubMed
-
- Arendt T, Bruckner MK, Krell T, Pagliusi S, Kruska L, Heumann R ( 1995) Degeneration of rat cholinergic basal forebrain neurons and reactive changes in nerve growth factor expression after chronic neurotoxic injury. II. Reactive expression of the nerve growth factor gene in astrocytes. Neuroscience 65: 647-659. - PubMed
-
- Cannella B, Pitt D, Marchionni M, Raine CS ( 1999) Neuregulin and erbB receptor expression in normal and diseased human white matter. J Neuroimmunol 100: 233-242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
