Baroreflex-induced sympathetic activation does not alter cerebrovascular CO2 responsiveness in humans
- PMID: 12844511
- PMCID: PMC2343219
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.046987
Baroreflex-induced sympathetic activation does not alter cerebrovascular CO2 responsiveness in humans
Abstract
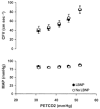
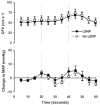
We investigated the effect of baroreflex-induced sympathetic activation, produced by lower body negative pressure (LBNP) at -40 mmHg, on cerebrovascular responsiveness to hyper- and hypocapnia in healthy humans. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound was used to measure blood flow velocity (CFV) in the middle cerebral artery during variations in end-tidal carbon dioxide pressure (PET,CO2) of +10, +5, 0, -5, and -10 mmHg relative to eupnoea. The slopes of the linear relationships between PET,CO2 and CFV were computed separately for hyper- and hypocapnia during the LBNP and no-LBNP conditions. LBNP decreased pulse pressure, but did not change mean arterial pressure. LBNP evoked an increase in ventilation that resulted in a 9 +/- 2 mmHg decrease in PET,CO2, which was corrected by CO2 supplementation of the inspired air. LBNP did not affect cerebrovascular CO2 response slopes during steady-state hypercapnia (3.14 +/- 0.24 vs. 2.96 +/- 0.26 cm s-1 mmHg-1) or hypocapnia (1.31 +/- 0.18 vs. 1.32 +/- 0.19 cm s-1 mmHg-1), or the CFV responses to voluntary apnoea (+51 +/- 19 vs. +50 +/- 18 %). Thus, cerebrovascular CO2 responsiveness was not altered by baroreflex-induced sympathetic activation. Our data challenge the concept that sympathetic activation restrains cerebrovascular responses to alterations in CO2 pressure.
Figures

Comment in
-
Perfusion of the human brain: a matter of interactions.J Physiol. 2003 Sep 1;551(Pt 2):402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.050609. Epub 2003 Jul 16. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12867571 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of the cerebrovascular response to apnoea in humans.J Physiol. 2003 Apr 1;548(Pt 1):323-32. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.029678. Epub 2003 Feb 14. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12588894 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
MRI measures of middle cerebral artery diameter in conscious humans during simulated orthostasis.Stroke. 2000 Jul;31(7):1672-8. doi: 10.1161/01.str.31.7.1672. Stroke. 2000. PMID: 10884472
-
Dynamic cerebral autoregulation and baroreflex sensitivity during modest and severe step changes in arterial PCO2.Brain Res. 2008 Sep 16;1230:115-24. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.07.048. Epub 2008 Jul 22. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18680730
-
Do acute stroke patients develop hypocapnia? A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neurol Sci. 2019 Jul 15;402:30-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2019.04.038. Epub 2019 Apr 30. J Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31102829
-
Integration of cerebrovascular CO2 reactivity and chemoreflex control of breathing: mechanisms of regulation, measurement, and interpretation.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009 May;296(5):R1473-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.91008.2008. Epub 2009 Feb 11. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19211719 Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebral blood flow changes associated with fluctuations in alpha and theta rhythm during sleep onset in humans.J Physiol. 2005 Oct 1;568(Pt 1):305-13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.092577. Epub 2005 Jul 7. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16002438 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral vasoreactivity: impact of heat stress and lower body negative pressure.Clin Auton Res. 2014 Jun;24(3):135-41. doi: 10.1007/s10286-014-0241-2. Epub 2014 Apr 6. Clin Auton Res. 2014. PMID: 24706257 Free PMC article.
-
Perfusion of the human brain: a matter of interactions.J Physiol. 2003 Sep 1;551(Pt 2):402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.050609. Epub 2003 Jul 16. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12867571 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The effect of changes in cardiac output on middle cerebral artery mean blood velocity at rest and during exercise.J Physiol. 2005 Dec 1;569(Pt 2):697-704. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.095836. Epub 2005 Oct 6. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16210355 Free PMC article.
-
Differential responses to CO2 and sympathetic stimulation in the cerebral and femoral circulations in humans.J Physiol. 2005 Jul 15;566(Pt 2):613-24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.087320. Epub 2005 May 12. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15890697 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ahn B, Sakakibara Y, Paulev PE, Masuda A, Nishibayashi Y, Nakamura W, Honda Y. Circulatory and respiratory responses to lower body negative pressure in man. Jpn J Physiol. 1989;39:919–929. - PubMed
-
- Aubineau PF, Sercombe R, Seylaz J. Continuous recordings of local cerebral blood flow during cervical sympathetic nerve blockade or stimulation. J Physiol. 1975;246:104–106P. - PubMed
-
- Baumbach GL, Heistad DD. Effects of sympathetic stimulation and changes in arterial pressure on segmental resistance of cerebral vessels in rabbits and cats. Circ Res. 1983;52:527–533. - PubMed
-
- Bishop CC, Powell S, Rutt D, Browse NL. Transcranial Doppler measurement of middle cerebral artery blood flow velocity: a validation study. Stroke. 1986;17:913–915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

