Bacteria-host communication: the language of hormones
- PMID: 12847292
- PMCID: PMC166419
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1537100100
Bacteria-host communication: the language of hormones
Abstract
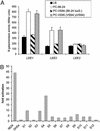
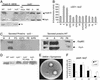
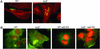
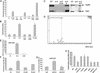
The interbacterial communication system known as quorum sensing (QS) utilizes hormone-like compounds referred to as autoinducers to regulate bacterial gene expression. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) serotype O157:H7 is the agent responsible for outbreaks of bloody diarrhea in several countries. We previously proposed that EHEC uses a QS regulatory system to "sense" that it is within the intestine and activate genes essential for intestinal colonization. The QS system used by EHEC is the LuxS/autoinducer 2 (AI-2) system extensively involved in interspecies communication. The autoinducer AI-2 is a furanosyl borate diester whose synthesis depends on the enzyme LuxS. Here we show that an EHEC luxS mutant, unable to produce the bacterial autoinducer, still responds to a eukaryotic cell signal to activate expression of its virulence genes. We have identified this signal as the hormone epinephrine and show that beta- and alpha-adrenergic antagonists can block the bacterial response to this hormone. Furthermore, using purified and in vitro synthesized AI-2 we showed that AI-2 is not the autoinducer involved in the bacterial signaling. EHEC produces another, previously undescribed autoinducer (AI-3) whose synthesis depends on the presence of LuxS. These results imply a potential cross-communication between the luxS/AI-3 bacterial QS system and the epinephrine host signaling system. Given that eukaryotic cell-to-cell signaling typically occurs through hormones, and that bacterial cell-to-cell signaling occurs through QS, we speculate that QS might be a "language" by which bacteria and host cells communicate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global effects of the cell-to-cell signaling molecules autoinducer-2, autoinducer-3, and epinephrine in a luxS mutant of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2007 Oct;75(10):4875-84. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00550-07. Epub 2007 Jul 16. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17635870 Free PMC article.
-
Autoinducer 3 and epinephrine signaling in the kinetics of locus of enterocyte effacement gene expression in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2006 Oct;74(10):5445-55. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00099-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16988219 Free PMC article.
-
AI-3 synthesis is not dependent on luxS in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2006 Aug;188(16):5668-81. doi: 10.1128/JB.00648-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16885435 Free PMC article.
-
SdiA sensing of acyl-homoserine lactones by enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) serotype O157:H7 in the bovine rumen.Gut Microbes. 2010 Nov-Dec;1(6):432-5. doi: 10.4161/gmic.1.6.14177. Gut Microbes. 2010. PMID: 21468228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum sensing and expression of virulence in Escherichia coli O157:H7.Int J Food Microbiol. 2003 Aug 15;85(1-2):1-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1605(02)00482-8. Int J Food Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12810266 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the potential environmental functions of viable but non-culturable bacteria.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Dec;29(12):2213-8. doi: 10.1007/s11274-013-1390-5. Epub 2013 Jun 4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23733177 Review.
-
Characterization of a ferrous iron-responsive two-component system in nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae.J Bacteriol. 2012 Nov;194(22):6162-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.01465-12. Epub 2012 Sep 7. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22961857 Free PMC article.
-
LsrR-mediated quorum sensing controls invasiveness of Salmonella typhimurium by regulating SPI-1 and flagella genes.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037059. Epub 2012 May 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22623980 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Norepinephrine on Mono-Species and Dual-Species Staphylococcal Biofilms.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 13;9(4):820. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040820. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33924447 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli is signaled by AI-2/LsrR: effects on small RNA and biofilm architecture.J Bacteriol. 2007 Aug;189(16):6011-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00014-07. Epub 2007 Jun 8. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17557827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaper, J. B. & O'Brien, A. D. (1998) Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Other Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli Strains (Am. Soc. Microbiol., Washington, DC). - PubMed
-
- Elliott, S. J., Wainwright, L. A., McDaniel, T. K., Jarvis, K. G., Deng, Y. K., Lai, L. C., McNamara, B. P., Donnenberg, M. S. & Kaper, J. B. (1998) Mol. Microbiol. 28, 1–4. - PubMed
-
- Mellies, J. L., Elliott, S. J., Sperandio, V., Donnenberg, M. S. & Kaper, J. B. (1999) Mol. Microbiol. 33, 296–306. - PubMed
-
- Sperandio, V., Mellies, J. L., Delahay, R. M., Frankel, G., Crawford, J. A., Nguyen, W. & Kaper, J. B. (2000) Mol. Microbiol. 38, 781–793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

