Effects of P-wave dispersion on atrial fibrillation in patients with acute anterior wall myocardial infarction
- PMID: 12848789
- PMCID: PMC6932667
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1542-474x.2003.08202.x
Effects of P-wave dispersion on atrial fibrillation in patients with acute anterior wall myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: P-wave dispersion (P dispersion), defined as the difference between the maximum and the minimum P-wave duration (P minimum), and maximum P-wave duration (P maximum) have been used to evaluate the discontinuous propagation of sinus impulse and the prolongation of atrial conduction time respectively. The aim of this study was to investigate whether early assessment of P dispersion predicts paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with acute anterior wall myocardial infarction (MI).
Methods: We prospectively evaluated 147 consecutive patients (45 women, 102 men; aged 55 +/- 9 years) with a first acute anterior wall MI. All patients were evaluated by echocardiography to measure the left atrial diameter and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Electrocardiography was recorded from all patients on admission and every day during hospitalization.
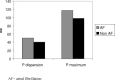
Results: AF occurred in 25 patients. In 122 patients, AF did not occur. P maximum was found to be significantly higher in patients with AF than in patients without AF (115 +/- 17.3 ms vs 101 +/- 14.7 ms, P = 0.001). P dispersion also was significantly higher in patients with AF than in patients without AF (50 +/- 12.5 ms vs 43 +/- 10.1 ms, P = 0.01). There was no significant difference between the two groups in P minimum (64 +/- 12.5 ms vs 59 +/- 11.7 ms, P = 0.057). The echocardiographically left atrial diameters were not significantly higher in the patients with AF than those without (25 +/- 3.38 mm and 23 +/- 3.36 mm, respectively, P = 0.76). LVEF was found to be significantly different in the patients who developed AF and in those who did not (37.96 +/- 6.18% vs 47.70 +/- 6.01%, P = 0.0001).
Conclusions: Although P maximum and P dispersion are significant predictive factors of AF in patients with acute anterior wall MI in the univariate analysis, on the basis of multivariate analysis, only age and LVEF were independent predictive parameters for AF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of stage of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction with P wave dispersion and occurrence of atrial fibrillation after first acute anterior myocardial infarction.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2004 Oct;9(4):330-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2004.94568.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2004. PMID: 15485510 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of reperfusion on P-wave duration and P-wave dispersion in acute myocardial infarction: primary angioplasty versus thrombolytic therapy.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005 Jan;10(1):35-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2005.00595.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005. PMID: 15649235 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
P wave dispersion on 12-lead electrocardiography in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2000 Jul;23(7):1109-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2000.tb00910.x. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10914366
-
P-wave dispersion: a novel predictor of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2001 Apr;6(2):159-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474x.2001.tb00101.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2001. PMID: 11333174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P-wave dispersion: an update.Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2016 Jul-Aug;16(4):126-133. doi: 10.1016/j.ipej.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2016. PMID: 27924760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of stage of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction with P wave dispersion and occurrence of atrial fibrillation after first acute anterior myocardial infarction.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2004 Oct;9(4):330-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2004.94568.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2004. PMID: 15485510 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic effects of perinatal asphyxia.Indian J Pediatr. 2014 Mar;81(3):231-3. doi: 10.1007/s12098-013-1328-9. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Indian J Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24519357 No abstract available.
-
Effect of reperfusion on P-wave duration and P-wave dispersion in acute myocardial infarction: primary angioplasty versus thrombolytic therapy.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005 Jan;10(1):35-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2005.00595.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005. PMID: 15649235 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of P-wave dispersion in healthy dogs, dogs with chronic valvular disease and dogs with disturbances of supraventricular conduction.Acta Vet Scand. 2011 Mar 11;53(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-53-18. Acta Vet Scand. 2011. PMID: 21396110 Free PMC article.
-
P-wave dispersion: What we know till now?JRSM Cardiovasc Dis. 2016 Mar 21;5:2048004016639443. doi: 10.1177/2048004016639443. eCollection 2016 Jan-Dec. JRSM Cardiovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 27081484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldberg RJ, Seeley D, Becker RC, et al Impact of atrial fibrillation on the in‐hospital and long‐term survival of patients with acute myocardial infarction: A community‐wide perspective. Am Heart J 1990;119: 996–1001. - PubMed
-
- Hod H, Lew AS, Keltai M, et al Early atrial fibrillation during evolving myocardial infarction: A consequence of impaired left atrial perfusion. Circulation 1987;75: 146–150. - PubMed
-
- Pritchett ELC. Management of atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 1992;326: 1264–1271. - PubMed
-
- Crenshaw BS, Ward SR, Granger CB, et al for the GUSTO‐1 Trial Investigators. Risk factors and outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation following acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997;30: 406–413. - PubMed
-
- Eldar M, Canetti M, Rotstein Z, et al Significance of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation complicating acute myocardial infarction in the thrombolytic era. Circulation 1998;97: 965–970. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical