Long-term improvement of QT dispersion is unaffected by short-term changes in blood pressure during treatment of systemic hypertension with enalapril
- PMID: 12848813
- PMCID: PMC6932356
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1542-474x.2003.08108.x
Long-term improvement of QT dispersion is unaffected by short-term changes in blood pressure during treatment of systemic hypertension with enalapril
Abstract
Background: We report the reduction of QT and QTc dispersion in patients treated for 7 years with enalapril for systemic hypertension with left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy. We assess the correlation between QT dispersion and LV mass during this period and at the end of an 8-week period of suspension of enalapril treatment after 5 years.
Methods: Twenty-four previously untreated patients with this condition took enalapril (20 mg twice daily) for 7 years, except during an 8-week period following 5-year follow-up. Cardiovascular parameters were determined by two-dimensional guided M-mode echocardiography, and QT interval was measured, in a pretreatment placebo phase, 8 weeks and 1, 3, 5, and 7 years after the start of the therapy, at the end of the 8-week suspension effected after 5 years, and 8 weeks after the end of the suspension.
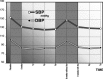
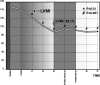
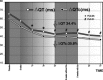
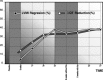
Results: Therapy rapidly reduced blood pressure (BP) from 156/105 mmHg to normal values: 134/84 mmHg after 8 weeks' treatment, 130-84 mmHg at 7-year follow-up (P < 0.001 with respect to the placebo phase). LV mass index decreased progressively until at 5-year follow-up the reduction had reached 39% (P < 0.001), after which neither LV mass nor any other structural parameter underwent any further significant change. During this time, QT dispersion (DeltaQT) and the dispersion of "corrected" QT (DeltaQTc) decreased significantly: DeltaQT (from 61 +/- 21 to 37 +/- 13 ms) and DeltaQTc (from 67 +/- 27 to 41 +/- 16 ms). After suspension of treatment for 8 weeks following 5-year follow-up, DeltaQT was 40 +/- 14 ms and DeltaQTc was 44 +/- 17 ms; there were no significant changes either in DeltaQT and DeltaQTc or LV hypertrophy although BP had returned to pretreatment values (BP: 150 +/- 16; 101 +/- 10 mmHg).
Conclusions: Long-term enalapril treatment of hypertensive patients with LV hypertrophy induces marked regression of LV mass and improvement of QT dispersion. These improvements occur on a longer timescale than improvement in BP, and are not affected by transient changes in BP values.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of QT and QTc dispersion during long-term treatment of systemic hypertension with enalapril.Am J Cardiol. 1998 Jan 15;81(2):170-4. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00869-2. Am J Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9591900
-
Left ventricular systolic function after marked reduction of ventricular hypertrophy induced by 5 years' enalapril treatment.Eur Heart J. 1995 Dec;16(12):1981-7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a060857. Eur Heart J. 1995. PMID: 8682036 Clinical Trial.
-
Maintenance of blood pressure control and left ventricular performance with small doses of enalapril.Am J Cardiol. 1999 Mar 1;83(5):719-23. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(98)00977-1. Am J Cardiol. 1999. PMID: 10080425
-
Step-down of enalapril treatment for arterial hypertension.Hypertension. 1999 Dec;34(6):1287-92. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.34.6.1287. Hypertension. 1999. PMID: 10601132 Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in left ventricular geometry during antihypertensive treatment.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Aug;134:193-199. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.06.026. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29959031 Review.
References
-
- Zabel M, Portnoy S, Franz M. Electrocardiographic indices of dispersion of ventricular repolarization: An isolated heart validation study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995;25: 746–752. - PubMed
-
- Statters DJ, Malik M, Ward DE, et al. QT dispersion: Problems of methodology and clinical significance. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 1994;5: 672–685. - PubMed
-
- Priori SG, Napolitano C, Diehl L, et al. Dispersion of the QT interval: A marker of therapeutic efficacy in the idiopathic long QT syndrome. Circulation 1994;89: 1681–1689. - PubMed
-
- Glancy JM, Garrant CJ, Woods KL, et al. QT dispersion and mortality after myocardial infarction. Lancet 1995;354: 945–948. - PubMed
-
- Perkiomaki JS, Koistinen J, Yli‐Mayri S, et al. Dispersion of QT interval in patients with and without susceptibility to ventricular tachyarrhythmias after previous myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995;26: 174–179. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

