Identification of an activator protein required for the induction of fruA, a gene essential for fruiting body development in Myxococcus xanthus
- PMID: 12851461
- PMCID: PMC166390
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1533026100
Identification of an activator protein required for the induction of fruA, a gene essential for fruiting body development in Myxococcus xanthus
Abstract
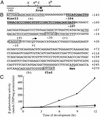
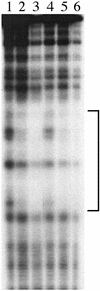
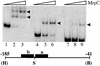
Myxococcus xanthus exhibits social behavior and multicellular development. FruA is an essential transcription factor for fruiting body development in M. xanthus. In the present study, the upstream promoter region was found to be necessary for the induction of fruA expression during development. A cis-acting element required for the induction was identified and was located between nucleotides -154 and -107 with respect to the transcription initiation site. In addition, it was found that two binding sites exist within this element of the fruA promoter. By using DNA affinity column chromatography containing the cis-acting element, a fruA promoter-binding protein was purified. The purified protein was shown by N-terminal sequence analysis to be identical to MrpC, a protein identified previously by transposon insertion mutagenesis as an essential locus for fruiting body development [Sun, H. & Shi, W. (2001) J. Bacteriol. 183, 4786-4795]. Furthermore, fruA mRNA was not detectable in the mrpC::km strain, demonstrating that MrpC is essential for fruA expression. Moreover, mutational analysis of the binding sites for MrpC in the fruA promoter indicates that binding of MrpC activates transcription of fruA in vivo. This report provides evidence for a direct molecular interaction involved in temporally regulated gene expression in M. xanthus.
Figures
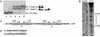


Similar articles
-
A protein Ser/Thr kinase cascade negatively regulates the DNA-binding activity of MrpC, a smaller form of which may be necessary for the Myxococcus xanthus development.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Jun;60(5):1205-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05178.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16689796
-
Dual regulation with Ser/Thr kinase cascade and a His/Asp TCS in Myxococcus xanthus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:111-21. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792684 Review.
-
Transcription factor MrpC binds to promoter regions of hundreds of developmentally-regulated genes in Myxococcus xanthus.BMC Genomics. 2014 Dec 16;15:1123. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1123. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25515642 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of FRUA expression during vegetative growth and development of Myxococcus xanthus.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003;5(2):87-96. doi: 10.1159/000069979. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 12736531
-
Intercellular signaling during fruiting-body development of Myxococcus xanthus.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1999;53:525-49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.53.1.525. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10547700 Review.
Cited by
-
Combinatorial regulation of fmgD by MrpC2 and FruA during Myxococcus xanthus development.J Bacteriol. 2011 Apr;193(7):1681-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01541-10. Epub 2011 Jan 21. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21257775 Free PMC article.
-
Milestones in the development of Myxococcus xanthus as a model multicellular bacterium.J Bacteriol. 2025 Jul 24;207(7):e0007125. doi: 10.1128/jb.00071-25. Epub 2025 Jun 17. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40525847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myxococcus xanthus developmental cell fate production: heterogeneous accumulation of developmental regulatory proteins and reexamination of the role of MazF in developmental lysis.J Bacteriol. 2012 Jun;194(12):3058-68. doi: 10.1128/JB.06756-11. Epub 2012 Apr 6. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22493014 Free PMC article.
-
GPI-Anchored Protein Homolog IcFBR1 Functions Directly in Morphological Development of Isaria cicadae.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Oct 31;8(11):1152. doi: 10.3390/jof8111152. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354919 Free PMC article.
-
Intra- and interprotein phosphorylation between two-hybrid histidine kinases controls Myxococcus xanthus developmental progression.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 20;287(30):25060-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.387241. Epub 2012 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22661709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dworkin, M. & Kaiser, D. (1993) Myxobacteria II (Am. Soc. Microbiol., Washington, DC).
-
- Shimkets, L. J. (1999) Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 53, 525–549. - PubMed
-
- Horiuchi, T., Taoka, M., Isobe, T., Komano, T. & Inouye, S. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 26753–26760. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa, M., Fujitani, S., Mao, X., Inouye, S. & Komano, T. (1996) Mol. Microbiol. 22, 757–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

