Early internal fixation and soft tissue cover of severe open tibial pilon fractures
- PMID: 12851785
- PMCID: PMC3461889
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-003-0486-1
Early internal fixation and soft tissue cover of severe open tibial pilon fractures
Abstract
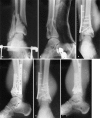
We studied 32 consecutive patients with open distal tibial pilon fractures. All patients had radical debridement with immediate skeletal stabilisation and early soft-tissue cover with a vascularized muscle flap. The minimum follow-up was 1 (range 1-8) year. There were four superficial infections, two deep infections and two amputations. There were no long-term problems with union and no patient required an ankle fusion. Patients were assessed using the SF-36 questionnaire. There were significant differences from the US norm in physical function score ( p<0.01), role physical score ( p<0.05) and physical component score ( p<0.01). Physical component score of 38.5 was significantly better ( p<0.01) when compared with amputees from severe lower-extremity trauma. Our protocol for management resulted in a good functional outcome with low infection and amputation rates.
Nous avons étudié 32 malades consécutifs avec une fracture ouverte du pilon tibial. Tous les malades avaient un débridement radical avec stabilisation squelettique immédiate et couverture tissulaire précoce avec un lambeau musculaire vascularisé. Le minimum de suivi était une année (1à 8 années). Il y avait 4 infections superficielles, 2 infections profondes et 2 amputations. Il n'y avait pas de problèmes de consolidation à long terme et aucune arthrodèse de cheville ne fut nécessaire. Les malades ont été étudiés à partir du questionnaire SF-36. Il y avait des différences significatives selon la norme américaine du score de la fonction physique (p<0.01), le rôle du score physique (p<0.05) et le score de la composante physique (p<0.01). Le score composant physique de 38.5 était considérablement meilleur (p<0.01) comparé aux amputés pour traumatisme distal sévére. Notre protocole de gestion de ces fractures a conduit à un bon résultat fonctionnel avec un taux d'infection et d'amputation très bas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fix and flap: the radical orthopaedic and plastic treatment of severe open fractures of the tibia.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000 Sep;82(7):959-66. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.82b7.10482. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000. PMID: 11041582
-
A staged protocol for soft tissue management in the treatment of complex pilon fractures.J Orthop Trauma. 2004 Sep;18(8 Suppl):S32-8. doi: 10.1097/00005131-200409001-00005. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. PMID: 15472563
-
A staged protocol for soft tissue management in the treatment of complex pilon fractures.J Orthop Trauma. 1999 Feb;13(2):78-84. doi: 10.1097/00005131-199902000-00002. J Orthop Trauma. 1999. PMID: 10052780
-
One-stage reconstruction of composite bone and soft-tissue defects in traumatic lower extremities.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004 Nov;114(6):1457-66. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000138811.88807.65. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. PMID: 15509933 Review.
-
[Fractures of the tibial pilon. Long-term retrospective study of 51 fractures treated with open reduction and osteosynthesis].Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1998 Apr;84(2):180-8. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1998. PMID: 9775062 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The Feasibility of 3D Printing Technology on the Treatment of Pilon Fracture and Its Effect on Doctor-Patient Communication.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jan 18;2018:8054698. doi: 10.1155/2018/8054698. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29581985 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Outcome of 28 open pilon fractures with injury severity-based fixation.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015 Apr;25(3):569-75. doi: 10.1007/s00590-014-1552-7. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015. PMID: 25256799
-
Management of high-energy tibial pilon fractures.Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2015 Nov;10(3):137-47. doi: 10.1007/s11751-015-0231-5. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2015. PMID: 26407690 Free PMC article.
-
The tibial bayonet method of wound closure.Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2018 Aug;13(2):103-108. doi: 10.1007/s11751-018-0304-3. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2018. PMID: 29363013 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of outcomes and complications of reconstruction and amputation for type IIIB and IIIC fractures of the tibia.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008 Dec;122(6):1796-1805. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31818d69c3. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008. PMID: 19050533 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

