Infection with Mycobacterium bovis BCG diverts traffic of myelin oligodendroglial glycoprotein autoantigen-specific T cells away from the central nervous system and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 12853387
- PMCID: PMC164279
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.10.4.564-572.2003
Infection with Mycobacterium bovis BCG diverts traffic of myelin oligodendroglial glycoprotein autoantigen-specific T cells away from the central nervous system and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
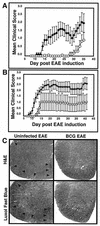
Infectious agents have been proposed to influence susceptibility to autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis. We induced a Th1-mediated central nervous system (CNS) autoimmune disease, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice with an ongoing infection with Mycobacterium bovis strain bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) to study this possibility. C57BL/6 mice infected with live BCG for 6 weeks were immunized with myelin oligodendroglial glycoprotein peptide (MOG(35-55)) to induce EAE. The clinical severity of EAE was reduced in BCG-infected mice in a BCG dose-dependent manner. Inflammatory-cell infiltration and demyelination of the spinal cord were significantly lessened in BCG-infected animals compared with uninfected EAE controls. ELISPOT and gamma interferon intracellular cytokine analysis of the frequency of antigen-specific CD4(+) T cells in the CNS and in BCG-induced granulomas and adoptive transfer of MOG(35-55)-specific green fluorescent protein-expressing cells into BCG-infected animals indicated that nervous tissue-specific (MOG(35-55)) CD4(+) T cells accumulate in the BCG-induced granuloma sites. These data suggest a novel mechanism for infection-mediated modulation of autoimmunity. We demonstrate that redirected trafficking of activated CNS antigen-specific CD4(+) T cells to local inflammatory sites induced by BCG infection modulates the initiation and progression of a Th1-mediated CNS autoimmune disease.
Figures
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, E., H. Isager, and K. Hyllested. 1981. Risk factors in multiple sclerosis: tuberculin reactivity, age at measles infection, tonsillectomy and appendectomy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 63:131-135. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Nun, A., I. Mendel, G. Sappler, and N. Kerlero de Rosbo. 1995. A 12-kDa protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis protects mice against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Protection in the absence of shared T cell epitopes with encephalitogenic proteins. J. Immunol. 154:2939-2948. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Nun, A., and S. Yossefi. 1992. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B as a potent suppressant of T lymphocytes: trace levels suppress T lymphocyte proliferative responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 22:1495-1503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

