Hippocampal cGMP-dependent protein kinase I supports an age- and protein synthesis-dependent component of long-term potentiation but is not essential for spatial reference and contextual memory
- PMID: 12853418
- PMCID: PMC6740356
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-14-06005.2003
Hippocampal cGMP-dependent protein kinase I supports an age- and protein synthesis-dependent component of long-term potentiation but is not essential for spatial reference and contextual memory
Abstract
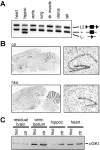
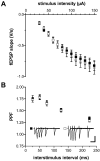
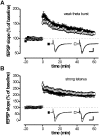
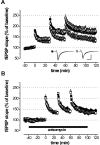
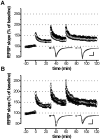
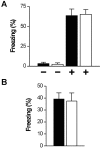
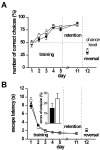
cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (cGKI) is expressed in the hippocampus, but its role in hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) is controversial. In addition, whether cGKI is involved in spatial learning has not been investigated. To address these issues, we generated mice with a hippocampus-specific deletion of cGKI (cGKIhko mice). Unlike conventional cGKI knock-out mice, cGKIhko mice lack gastrointestinal and cardiovascular phenotypes and have a normal life expectancy, which enables us to analyze hippocampal synaptic plasticity and learning in young and adult animals. Hippocampal LTP after repetitive episodes of theta burst stimulation was impaired in adult (12-14 weeks of age) but not in juvenile (3-4 weeks of age) cGKIhko mice. The difference in LTP between adult control and cGKIhko mice was abolished by the protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin, suggesting that the impairment of LTP in adult cGKIhko mice reflects a defect in late-phase LTP. Despite their deficit in LTP, adult cGKIhko mutants showed normal performance in a discriminatory water maze and had intact contextual fear conditioning. These results suggest that hippocampal cGKI supports an age- and protein synthesis-dependent form of hippocampal LTP, whereas it is dispensable for hippocampus-dependent spatial reference and contextual memory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signaling through cGMP-dependent protein kinase I in the amygdala is critical for auditory-cued fear memory and long-term potentiation.J Neurosci. 2008 Dec 24;28(52):14202-12. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2216-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19109502 Free PMC article.
-
Protein synthesis is required for the enhancement of long-term potentiation and long-term memory by spaced training.J Neurophysiol. 2002 Jun;87(6):2770-7. doi: 10.1152/jn.2002.87.6.2770. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 12037179
-
Neuropsin is essential for early processes of memory acquisition and Schaffer collateral long-term potentiation in adult mouse hippocampus in vivo.J Physiol. 2006 Feb 1;570(Pt 3):541-51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.098715. Epub 2005 Nov 24. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16308352 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential activation of soluble guanylate cyclase, protein kinase G and cGMP-degrading phosphodiesterase is necessary for proper induction of long-term potentiation in CA1 of hippocampus. Alterations in hyperammonemia.Neurochem Int. 2004 Nov;45(6):895-901. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2004.03.020. Neurochem Int. 2004. PMID: 15312984 Review.
-
Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014 Mar;15(3):181-92. doi: 10.1038/nrn3677. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24552786 Review.
Cited by
-
cGMP-dependent protein kinase I, the circadian clock, sleep and learning.Commun Integr Biol. 2009 Jul;2(4):298-301. doi: 10.4161/cib.2.4.8220. Commun Integr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19721870 Free PMC article.
-
Case-control genome-wide association study of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010 Sep;49(9):906-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2010.06.007. Epub 2010 Aug 5. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20732627 Free PMC article.
-
Role of hippocampal Cav1.2 Ca2+ channels in NMDA receptor-independent synaptic plasticity and spatial memory.J Neurosci. 2005 Oct 26;25(43):9883-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1531-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16251435 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cGMP-dependent signaling pathway in synaptic vesicle cycle at the frog motor nerve terminals.J Neurosci. 2008 Dec 3;28(49):13216-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2947-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19052213 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors against Neurodegeneration: The Perspective of the Medicinal Chemist.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Jun 17;11(12):1726-1739. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00244. Epub 2020 May 28. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32401481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arancio O, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD ( 1995) Activity-dependent long-term enhancement of transmitter release by presynaptic 3′, 5′-cyclic GMP in cultured hippocampal neurons. Nature 376: 74–80. - PubMed
-
- Arancio O, Kiebler M, Lee CJ, Lev-Ram V, Tsien RY, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD ( 1996) Nitric oxide acts directly in the presynaptic neuron to produce long-term potentiation in cultured hippocampal neurons. Cell 87: 1025–1035. - PubMed
-
- Arns M, Sauvage M, Steckler T ( 1999) Excitotoxic hippocampal lesions disrupt allocentric spatial learning in mice: effects of strain and task demands. Behav Brain Res 106: 151–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
