Light-evoked excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs to ON and OFF alpha ganglion cells in the mouse retina
- PMID: 12853425
- PMCID: PMC6740343
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-14-06063.2003
Light-evoked excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs to ON and OFF alpha ganglion cells in the mouse retina
Abstract
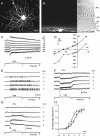
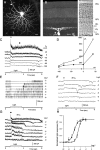
Bipolar cell and amacrine cell synaptic inputs to alpha ganglion cells (alphaGCs) in dark-adapted mouse retinas were studied by recording the light-evoked excitatory cation current (DeltaIC) and inhibitory chloride current (DeltaICl) under voltage-clamp conditions, and the cell morphology was revealed by Lucifer yellow fluorescence with a confocal microscope. Three types of alphaGCs were identified. (1) ONalphaGCs exhibits no spike activity in darkness, increased spikes in light, sustained inward DeltaIC, sustained outward DeltaICl of varying amplitude, and large soma (20-25 microm in diameter) with alpha-cell-like dendritic field approximately 180-350 microm stratifying near 70% of the inner plexiform layer (IPL) depth. (2) Transient OFFalphaGCs (tOFFalphaGCs) exhibit no spike activity in darkness, transient increased spikes at light offset, small sustained outward DeltaIC in light, a large transient inward DeltaIC at light offset, a sustained outward DeltaICl, and a morphology similar to the ONalphaGCs except for that their dendrites stratified near 30% of the IPL depth. (3) Sustained OFFalphaGCs exhibit maintained spike activity of 5-10 Hz in darkness, sustained decrease of spikes in light, sustained outward DeltaIC, sustained outward DeltaICl, and a morphology similar to the tOFFalphaGCs. By comparing the response thresholds and dynamic ranges of alphaGCs with those of the preganglion cells, our data suggest that the light responses of each type of alphaGCs are mediated by different sets of bipolar cells and amacrine cells. This detailed physiological analysis complements the existing anatomical results and provides new insights on the functional roles of individual synapses in the inner mammalian retina.
Figures


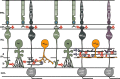
 (red), electrical synapses; PRL, photoreceptor layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer (a, sublamina a; b, sublamina b); GCL, ganglion cell layer.
(red), electrical synapses; PRL, photoreceptor layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer (a, sublamina a; b, sublamina b); GCL, ganglion cell layer.References
-
- Applebury ML, Antoch MP, Baxter LC, Chun LL, Falk JD, Farhangfar F, Kage K, Krzystolik MG, Lyass LA, Robbins JT ( 2000) The murine cone photoreceptor: a single cone type expresses both S and M opsins with retinal spatial patterning. Neuron 27: 513–523. - PubMed
-
- Baylor DA ( 1987) Photoreceptor signals and vision. Proctor lecture [review]. Invest Ophthal Vis Sci 28: 34–49. - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield SA, Dacheux RF ( 2001) Rod vision: pathways and processing in the mammalian retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 20: 351–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
