Imprinted silencing of Slc22a2 and Slc22a3 does not need transcriptional overlap between Igf2r and Air
- PMID: 12853484
- PMCID: PMC165611
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg341
Imprinted silencing of Slc22a2 and Slc22a3 does not need transcriptional overlap between Igf2r and Air
Abstract
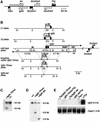
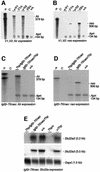
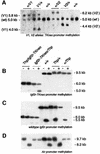
Silencing of the paternal allele of three imprinted genes (Igf2r, Slc22a2 and Slc22a3) requires cis expression of the Air RNA that overlaps the promoter of one of them (Igf2r). Air is a non-coding RNA whose mode of action is unknown. We tested the role of the Igf2r promoter and the role of transcriptional overlap between Igf2r and Air in silencing in this cluster. We analyzed imprinted expression in mice in which the Igf2r promoter is replaced by a thymidine kinase promoter that preserves a transcription overlap with Air, and in mice with a deleted Igf2r promoter that lack any transcriptional overlap with Air. Imprinted silencing of Air, Slc22a2 and Slc22a3 is maintained by the replacement promoter and also in the absence of transcriptional overlap with Air. These results exclude a role for the Igf2r promoter and for transcriptional overlap between Igf2r and Air in silencing Air, Slc22a2 and Slc22a3. Although these results do not completely exclude a role for a double-stranded RNA silencing mechanism, they do allow the possibility that the Air RNA has intrinsic cis silencing properties.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The non-coding Air RNA is required for silencing autosomal imprinted genes.Nature. 2002 Feb 14;415(6873):810-3. doi: 10.1038/415810a. Nature. 2002. PMID: 11845212
-
Genomic imprinting of the IGF2R/AIR locus is conserved between bovines and mice.Theriogenology. 2022 Mar 1;180:121-129. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2021.12.013. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Theriogenology. 2022. PMID: 34971973
-
Long-range DNase I hypersensitivity mapping reveals the imprinted Igf2r and Air promoters share cis-regulatory elements.Genome Res. 2005 Oct;15(10):1379-87. doi: 10.1101/gr.3783805. Genome Res. 2005. PMID: 16204191 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-species clues of an epigenetic imprinting regulatory code for the IGF2R gene.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006;113(1-4):202-8. doi: 10.1159/000090833. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 16575181 Review.
-
Epigenetics of imprinted long noncoding RNAs.Epigenetics. 2009 Jul 1;4(5):277-86. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Epigenetics. 2009. PMID: 19617707 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic imprinting-an epigenetic gene-regulatory model.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010 Apr;20(2):164-70. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010. PMID: 20153958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imprinted noncoding RNAs.Mamm Genome. 2008 Aug;19(7-8):493-502. doi: 10.1007/s00335-008-9139-4. Epub 2008 Sep 25. Mamm Genome. 2008. PMID: 18815833 Review.
-
Transcription is required for establishment of germline methylation marks at imprinted genes.Genes Dev. 2009 Jan 1;23(1):105-17. doi: 10.1101/gad.495809. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19136628 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic dynamics during preimplantation development.Reproduction. 2015 Sep;150(3):R109-20. doi: 10.1530/REP-15-0180. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Reproduction. 2015. PMID: 26031750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paramutation: the chromatin connection.Plant Cell. 2004 Jun;16(6):1358-64. doi: 10.1105/tpc.160630. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15178748 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Avner P. and Heard,E. (2001) X-chromosome inactivation: counting, choice and initiation. Nat. Rev. Genet., 2, 59–67. - PubMed
-
- Beechey C.V., Cattanach,B.M. and Blake,A. (2001) MRC Mammalian Genetics Unit, Harwell, Oxfordshire. World Wide Web Site—Mouse Imprinting Data and References (http://www.mgu.har.mrc.ac.uk/imprinting/imprinting.html).
-
- Bell A.C., West,A.G. and Felsenfeld,G. (2001) Insulators and boundaries: versatile regulatory elements in the eukaryotic genome. Science, 291, 447–450. - PubMed
-
- Benzow K.A. and Koob,M.D. (2002) The KLHL1-antisense transcript (KLHL1AS) is evolutionarily conserved. Mamm. Genome, 13, 134–141. - PubMed
-
- Engemann S., Strodicke,M., Paulsen,M., Franck,O., Reinhardt,R., Lane,N., Reik,W. and Walter,J. (2000) Sequence and functional comparison in the Beckwith–Wiedemann region: implications for a novel imprinting centre and extended imprinting. Hum. Mol. Genet., 9, 2691–2706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

