Vertebrate HoxB gene expression requires DNA replication
- PMID: 12853488
- PMCID: PMC165622
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg352
Vertebrate HoxB gene expression requires DNA replication
Abstract
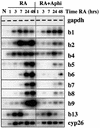
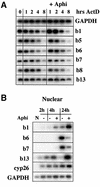
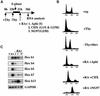
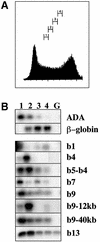
To study the relationship between DNA replication and transcription in vivo, we investigated Hox gene activation in two vertebrate systems: the embryogenesis of Xenopus and the retinoic acid-induced differentiation of pluripotent mouse P19 cells. We show that the first cell cycles following the mid- blastula transition in Xenopus are necessary and sufficient for HoxB activation, whereas later cell cycles are necessary for the correct expression pattern. In P19 cells, HoxB expression requires proliferation, and the entire locus is activated within one cell cycle. Using synchronous cultures, we found that activation of HoxB genes is colinear within a single cell cycle, occurs during S phase and requires S phase. The HoxB locus replicates early, whereas replication is still required for maximal expression later in S phase. Thus, induction of HoxB genes occurs in a DNA replication-dependent manner and requires only one cell cycle. We propose that S-phase remodelling licenses the locus for transcriptional regulation.
Figures





References
-
- Ambros V. (1999) Cell cycle-dependent sequencing of cell fate decisions in Caenorhabditis elegans vulva precursor cells. Development, 126, 1947–1956. - PubMed
-
- Bel-Vialar S., Itasaki,N. and Krumlauf,R. (2002) Initiating Hox gene expression: in the early chick neural tube differential sensitivity to FGF and RA signaling subdivides the HoxB genes into two distinct groups. Development, 129, 5103–5115. - PubMed
-
- Berg R.W. and McBurney,M.W. (1990) Cell density and cell cycle effects on retinoic acid-induced embryonal carcinoma cell differentiation. Dev. Biol., 138, 123–135. - PubMed
-
- Boterenbrood E.C., Narraway,J. and Hara,K. (1983) Duration of cleavage cycles and asymmetry in the direction of cleavage waves prior to gastrulation in Xenopus laevis. Roux Arch. Dev. Biol., 192, 216–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

