Sm-like proteins in Eubacteria: the crystal structure of the Hfq protein from Escherichia coli
- PMID: 12853626
- PMCID: PMC167641
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg480
Sm-like proteins in Eubacteria: the crystal structure of the Hfq protein from Escherichia coli
Abstract
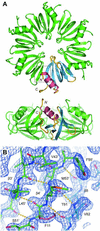
The Hfq protein was discovered in Escherichia coli in the early seventies as a host factor for the Qbeta phage RNA replication. During the last decade, it was shown to be involved in many RNA processing events and remote sequence homology indicated a link to spliceosomal Sm proteins. We report the crystal structure of the E.coli Hfq protein showing that its monomer displays a characteristic Sm-fold and forms a homo-hexamer, in agreement with former biochemical data. Overall, the structure of the E.coli Hfq ring is similar to the one recently described for Staphylococcus aureus. This confirms that bacteria contain a hexameric Sm-like protein which is likely to be an ancient and less specialized form characterized by a relaxed RNA binding specificity. In addition, we identified an Hfq ortholog in the archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii which lacks a classical Sm/Lsm gene. Finally, a detailed structural comparison shows that the Sm-fold is remarkably well conserved in bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya, and represents a universal and modular building unit for oligomeric RNA binding proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An Hfq-like protein in archaea: crystal structure and functional characterization of the Sm protein from Methanococcus jannaschii.RNA. 2007 Dec;13(12):2213-23. doi: 10.1261/rna.689007. Epub 2007 Oct 24. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17959927 Free PMC article.
-
Predicted structure and phyletic distribution of the RNA-binding protein Hfq.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Sep 1;30(17):3662-71. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf508. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12202750 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional structures of fibrillar Sm proteins: Hfq and other Sm-like proteins.J Mol Biol. 2006 Feb 10;356(1):86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.11.010. Epub 2005 Nov 22. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16337963
-
Hfq structure, function and ligand binding.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Apr;10(2):125-33. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.03.015. Epub 2007 Mar 28. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17395525 Review.
-
The bacterial Sm-like protein Hfq: a key player in RNA transactions.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Mar;51(6):1525-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2003.03935.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15009882 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into the recognition of the internal A-rich linker from OxyS sRNA by Escherichia coli Hfq.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Feb 27;43(4):2400-11. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv072. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25670676 Free PMC article.
-
Hfq-bridged ternary complex is important for translation activation of rpoS by DsrA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jun;41(11):5938-48. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt276. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23605038 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin Gallate Remodelling of Hfq Amyloid-Like Region Affects Escherichia coli Survival.Pathogens. 2018 Dec 1;7(4):95. doi: 10.3390/pathogens7040095. Pathogens. 2018. PMID: 30513780 Free PMC article.
-
Hfq C-terminal region forms a β-rich amyloid-like motif without perturbing the N-terminal Sm-like structure.Commun Biol. 2023 Oct 21;6(1):1075. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05462-1. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37865695 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of Hfq from Bacillus subtilis in complex with SELEX-derived RNA aptamer: insight into RNA-binding properties of bacterial Hfq.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(4):1856-67. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr892. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22053080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franze de Fernandez M.T., Hayward,W.S. and August,J.T. (1972) Bacterial proteins required for replication of phage Q ribonucleic acid. Purification and properties of host factor I, a ribonucleic acid-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem., 247, 824–831. - PubMed
-
- Tsui H.C., Leung,H.C. and Winkler,M.E. (1994) Characterization of broadly pleiotropic phenotypes caused by an hfq insertion mutation in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol. Microbiol., 13, 35–49. - PubMed
-
- Muffler A., Fischer,D. and Hengge-Aronis,R. (1996) The RNA-binding protein HF-I, known as a host factor for phage Qbeta RNA replication, is essential for rpoS translation in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev., 10, 1143–1151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

