GAGA facilitates binding of Pleiohomeotic to a chromatinized Polycomb response element
- PMID: 12853632
- PMCID: PMC167640
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg479
GAGA facilitates binding of Pleiohomeotic to a chromatinized Polycomb response element
Abstract
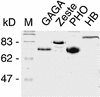
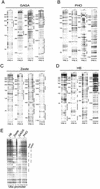
Polycomb response elements (PREs) are chromosomal elements, typically comprising thousands of base pairs of poorly defined sequences that confer the maintenance of gene expression patterns by Polycomb group (PcG) repressors and trithorax group (trxG) activators. Genetic studies have indicated a synergistic requirement for the trxG protein GAGA and the PcG protein Pleiohomeotic (PHO) in silencing at several PREs. However, the molecular basis of this cooperation remains unknown. Here, using DNaseI footprinting analysis, we provide a high-resolution map of sites for the sequence- specific DNA-binding PcG protein PHO, trxG proteins GAGA and Zeste and the gap protein Hunchback (HB) on the 1.6 kb Ultrabithorax (Ubx) PRE. Although these binding elements are present throughout the PRE, they display clear patterns of clustering, suggestive of functional collaboration at the level of PRE binding. We found that while GAGA could efficiently bind to a chromatinized PRE, PHO alone was incapable of binding to chromatin. However, PHO binding to chromatin, but not naked DNA, was strongly facilitated by GAGA, indicating interdependence between GAGA and PHO already at the level of PRE binding. These results provide a biochemical explanation for the in vivo cooperation between GAGA and PHO and suggest that PRE function involves the integrated activities of genetically antagonistic trxG and PcG proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of Polycomb group complexes by the sequence-specific DNA binding proteins Zeste and GAGA.Genes Dev. 2003 Nov 15;17(22):2741-6. doi: 10.1101/gad.1143303. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 14630938 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila pho-like gene encodes a YY1-related DNA binding protein that is redundant with pleiohomeotic in homeotic gene silencing.Development. 2003 Jan;130(2):285-94. doi: 10.1242/dev.00204. Development. 2003. PMID: 12466196
-
Recruitment of Drosophila Polycomb group proteins to chromatin by DSP1.Nature. 2005 Mar 24;434(7032):533-8. doi: 10.1038/nature03386. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15791260
-
Heritable chromatin states induced by the Polycomb and trithorax group genes.Novartis Found Symp. 1998;214:51-61; discussion 61-6, 104-13. doi: 10.1002/9780470515501.ch4. Novartis Found Symp. 1998. PMID: 9601011 Review.
-
Polycomb response elements and targeting of Polycomb group proteins in Drosophila.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006 Oct;16(5):476-84. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2006.08.005. Epub 2006 Aug 17. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006. PMID: 16914306 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic recognition of an epigenetic DNA element by Pleiohomeotic and a Polycomb core complex.Genes Dev. 2005 Aug 1;19(15):1755-60. doi: 10.1101/gad.347005. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 16077005 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb and Trithorax Group Genes in Drosophila.Genetics. 2017 Aug;206(4):1699-1725. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.185116. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28778878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replacement of a Drosophila Polycomb response element core, and in situ analysis of its DNA motifs.Mol Genet Genomics. 2008 Jun;279(6):595-603. doi: 10.1007/s00438-008-0336-3. Epub 2008 Mar 19. Mol Genet Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18350319
-
Are we there yet? Initial targeting of the Male-Specific Lethal and Polycomb group chromatin complexes in Drosophila.Open Biol. 2014 Mar 26;4(3):140006. doi: 10.1098/rsob.140006. Open Biol. 2014. PMID: 24671948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb group response elements in Drosophila and vertebrates.Adv Genet. 2013;81:83-118. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407677-8.00003-8. Adv Genet. 2013. PMID: 23419717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bienz M. and Muller,J. (1995) Transcriptional silencing of homeotic genes in Drosophila. Bioessays, 17, 775–784. - PubMed
-
- Brock H.W. and van Lohuizen,M. (2001) The Polycomb group–no longer an exclusive club? Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 11, 175–181. - PubMed
-
- Francis N.J. and Kingston,R.E. (2001) Mechanisms of transcriptional memory. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2, 409–421. - PubMed
-
- Kennison J.A. (1995) The Polycomb and trithorax group proteins of Drosophila: trans-regulators of homeotic gene function. Annu. Rev. Genet., 29, 289–303. - PubMed
-
- Lyko F. and Paro,R. (1999) Chromosomal elements conferring epigenetic inheritance. Bioessays, 21, 824–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

