Heteromeric MAPPIT: a novel strategy to study modification-dependent protein-protein interactions in mammalian cells
- PMID: 12853652
- PMCID: PMC167658
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gng075
Heteromeric MAPPIT: a novel strategy to study modification-dependent protein-protein interactions in mammalian cells
Abstract
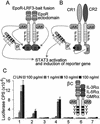
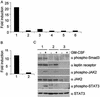
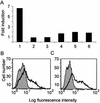
We recently reported a two-hybrid trap for detecting protein-protein interactions in intact mammalian cells (MAPPIT). The bait protein was fused to a STAT recruitment-deficient, homodimeric cytokine receptor and the prey protein to functional STAT recruitment sites. In such a configuration, STAT-dependent responses can be used to monitor a given bait-prey interaction. Using this system, we were able to demonstrate both modification-independent and tyrosine phosphorylation- dependent interactions. Protein modification in this approach is, however, strictly dependent on the receptor-associated JAK tyrosine kinases. We have now extended this concept by using extracellular domains of the heteromeric granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (GM-CSFR). Herein, the bait was fused to the (beta)c chain and its modifying enzyme to the GM-CSFRalpha chain (or vice versa). We demonstrate several serine phosphorylation-dependent interactions in the TGFbeta/Smad pathway using the catalytic domains of the ALK4 or ALK6 serine/threonine kinase receptors. In all cases tested, STAT-dependent signaling was completely abolished when mutant baits were used wherein critical serine residues were replaced by alanines. This approach operates both in transient and stable expression systems and may not be limited to serine phosphorylation but has the potential for studying various different types of protein modification-dependent interactions in intact cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation of Shc is not required for proliferation or viability signaling by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in hematopoietic cell lines.J Immunol. 1996 Jul 15;157(2):534-40. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8752899
-
Distinct domains of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor alpha subunit mediate activation of Jak/Stat signaling and differentiation.Blood. 2001 Mar 15;97(6):1662-70. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.6.1662. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11238105
-
A systematic scan of interactions with tyrosine motifs in the erythropoietin receptor using a mammalian 2-hybrid approach.Blood. 2005 Jun 1;105(11):4264-71. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2733. Epub 2005 Jan 11. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15644415
-
Dissociation of the Jak kinase pathway from G-CSF receptor signaling in neutrophils.Exp Hematol. 1997 Feb;25(2):160-8. Exp Hematol. 1997. PMID: 9015216
-
MAPPIT: a protein interaction toolbox built on insights in cytokine receptor signaling.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011 Oct-Dec;22(5-6):321-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2011.11.001. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011. PMID: 22119007 Review.
Cited by
-
Random mutagenesis MAPPIT analysis identifies binding sites for Vif and Gag in both cytidine deaminase domains of Apobec3G.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044143. Epub 2012 Sep 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22970171 Free PMC article.
-
Straightforward Protein-Protein Interaction Interface Mapping via Random Mutagenesis and Mammalian Protein Protein Interaction Trap (MAPPIT).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 26;20(9):2058. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092058. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31027327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application guide for omics approaches to cell signaling.Nat Chem Biol. 2015 Jun;11(6):387-97. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1809. Epub 2015 May 15. Nat Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25978996
-
Definition of the interacting interfaces of Apobec3G and HIV-1 Vif using MAPPIT mutagenesis analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Apr;38(6):1902-12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1154. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20015971 Free PMC article.
-
An experimentally derived confidence score for binary protein-protein interactions.Nat Methods. 2009 Jan;6(1):91-7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1281. Epub 2008 Dec 7. Nat Methods. 2009. PMID: 19060903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fields S. and Song,O. (1989) A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature, 340, 245–246. - PubMed
-
- Broder Y.C., Katz,S. and Aronheim,A. (1998) The ras recruitment system, a novel approach to the study of protein-protein interactions. Curr. Biol., 8, 1121–1124. - PubMed
-
- Osborne M.A., Dalton,S. and Kochan,J.P. (1995) The yeast tribrid system—genetic detection of trans-phosphorylated ITAM-SH2-interactions. Biotechnology, 13, 1474–1478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

