Simultaneous on/off regulation of transgenes located on a mammalian chromosome with Cre-expressing adenovirus and a mutant loxP
- PMID: 12853653
- PMCID: PMC167663
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gng076
Simultaneous on/off regulation of transgenes located on a mammalian chromosome with Cre-expressing adenovirus and a mutant loxP
Abstract
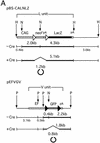
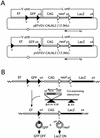
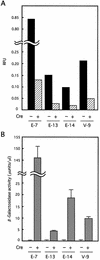
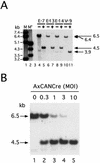
The site-specific recombinase Cre has often been used for on/off regulation of expression of transgenes introduced into the mammalian chromosome. However, this method is only applicable to the regulation of a single gene and cannot be used to simultaneously regulate two genes, because site-specific recombination occurs from the target loxP sequence of one regulating unit to the loxP sequence of any other unit and would eventually disrupt the structure of both regulating units. We previously reported a mutant loxP sequence with a two base substitution called loxP V (previously called loxP 2272), with which wild-type loxP cannot recombine but with which the identical mutant loxP recombines efficiently. In the present study we isolated cell lines bearing two regulating units on a chromosome containing a pair of wild-type loxP sequences or mutant loxP V sequences. After infection with Cre-expressing recombinant adenovirus AxCANCre, expression of a gene in each regulating unit was simultaneously turned on and off. Southern analyses showed that both regulating units were processed simultaneously and independently, even after infection with a limited amount of AxCANCre. The results showed that simultaneous regulation of gene expression on a mammalian chromosome mediated by Cre can be achieved by using mutant loxP V and wild-type loxP. This method may be a useful approach for conditional transgenic/knockout animals and investigation of gene function involving two genes simultaneously. Another possible application is for preparation of a new packaging cell line of viral vectors through simultaneous production of toxic viral genes.
Figures



References
-
- Sternberg N. and Hamilton,D. (1981) Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. I. Recombination between loxP sites. J. Mol. Biol., 150, 467–486. - PubMed
-
- Barinaga M. (1994) Knockout mice: round two. Science, 265, 26–28. - PubMed
-
- Rossant J. and Nagy,A. (1995) Genome engineering: the new mouse genetics. Nature Med., 1, 592–594. - PubMed
-
- Lewandoski M. (2001) Conditional control of gene expression in the mouse. Nature Rev. Genet., 2, 743–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

