Rho-dependent kinase is involved in agonist-activated calcium entry in rat arteries
- PMID: 12853654
- PMCID: PMC2343281
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.047050
Rho-dependent kinase is involved in agonist-activated calcium entry in rat arteries
Abstract
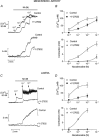
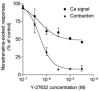
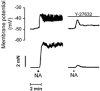
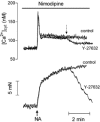
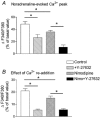
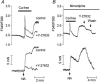
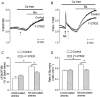
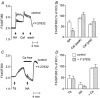
The present study was aimed at investigating whether, besides its pivotal role in Ca(2+)-independent contraction of smooth muscle, Rho-kinase is involved in the mechanisms underlying the Ca2+ signal activated by noradrenaline in arteries. In rat aorta and mesenteric artery, the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (10 microM) completely relaxed the contraction evoked by noradrenaline (1 microM) and simultaneously inhibited the Ca2+ signal by 54 +/- 1 % (mesenteric artery) and 71 +/- 15 % (aorta), and the cell membrane depolarisation by 56 +/- 11 % (mesenteric artery). A similar effect was observed in arteries contracted by AlF4-, while in KCl-contracted arteries, Y-27632 decreased tension without changing cytosolic Ca2+. The same effects were observed with another inhibitor of Rho-kinase (HA1077) but not with an inhibitor of protein kinase C (Ro-31-8220). Effects of Y-27632 were not prevented by incubating the artery in 25 mM KCl, with K+ channel blockers or with the Ca2+ channel blocker nimodipine. Y-27632 did not affect either the increase in the production of inositol phosphates activated by noradrenaline, or the release of Ca2+ from non-mitochondrial stores evoked by InsP3 in permeabilised aortic cells, or the Ca2+ signals evoked by thapsigargin or caffeine. The capacitative Ca2+ entry activated by thapsigargin was not impaired by Y-27632, but the entry of Ba2+ activated by noradrenaline in the presence of nimodipine was blocked by 10 microM Y-27632. These results indicate that Rho-kinase is involved in noradrenaline activation of a Ca2+ entry distinct from voltage- or store-operated channels in rat arteries.
Figures
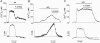

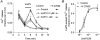
Similar articles
-
Role of Rho-kinase in guinea-pig gallbladder smooth muscle contraction.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Mar 18;534(1-3):210-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.01.016. Epub 2006 Feb 24. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16499905
-
Regulation of capacitative and noncapacitative receptor-operated Ca2+ entry by rho-kinase in tracheal smooth muscle.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002 Apr;26(4):491-8. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.26.4.4701. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11919086
-
Brazilein-induced contraction of rat arterial smooth muscle involves activation of Ca2+ entry and ROK, ERK pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Feb 12;580(3):366-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.012. Epub 2007 Nov 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18177858
-
Smooth muscle contraction by small GTPase Rho.Nagoya J Med Sci. 2002 May;65(1-2):1-8. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2002. PMID: 12083286 Review.
-
Vasomotion and underlying mechanisms in small arteries. An in vitro study of rat blood vessels.Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1993;614:1-44. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1993. PMID: 8128886 Review.
Cited by
-
A truncated tropomyosin-related kinase B receptor, T1, regulates glial cell morphology via Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor 1.J Neurosci. 2005 Feb 9;25(6):1343-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4436-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15703388 Free PMC article.
-
Regional heterogeneity in the mechanisms of myogenic tone in hamster arterioles.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;313(3):H667-H675. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00183.2017. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28667050 Free PMC article.
-
Flavone Attenuates Vascular Contractions by Inhibiting RhoA/Rho Kinase Pathway.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;13(3):201-7. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.3.201. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19885038 Free PMC article.
-
Failure of Bay K 8644 to induce RhoA kinase-dependent calcium sensitization in rabbit blood vessels.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jul;160(6):1326-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00751.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20590624 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of RhoA/Rho kinase inhibitors in pulmonary hypertension.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;155(4):444-54. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.239. Epub 2008 Jun 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18536743 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boonen HC, De Mey JG. G-proteins are involved in contractile responses of isolated mesenteric resistance arteries to agonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990;342:462–468. - PubMed
-
- Boulay G, Zhu X, Peyton M, Jiang M, Hurst R, Stefani E, Birnbaumer L. Cloning and expression of a novel mammalian homolog of Drosophila transient receptor potential (Trp) involved in calcium entry secondary to activation of receptors coupled by the Gq class of G protein. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29672–29680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

