Correlates of immune activation marker changes in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-seropositive and high-risk HIV-seronegative women who use illicit drugs
- PMID: 12854075
- PMCID: PMC3164115
- DOI: 10.1086/376509
Correlates of immune activation marker changes in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-seropositive and high-risk HIV-seronegative women who use illicit drugs
Abstract
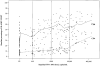
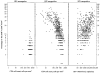
The majority of natural history studies of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection have immune and viral parameters in men. Data demonstrating that women have lower HIV-1 RNA levels than men at the same CD4 cell counts have raised the question of immunologic differences in HIV-seropositive women. This study describes levels and changes in phenotypic markers of immune maturity, function, and activation in the CD4 and CD8 cell subsets in HIV-seropositive and high-risk HIV-seronegative women. Our primary hypothesis was that activation levels would be significantly higher among illicit drug users. However, results showed that HIV-1 RNA level was the strongest predictor of marker level and that both HIV-1 RNA level and CD4 cell count were independently associated with CD4 activation, but illicit drug use was not. In summary, this study demonstrated that immune activation was a significant pathogenic feature in women and that activation was driven by HIV infection and not illicit drug use.
Figures
References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–60. - PubMed
-
- Lyles RH, Munoz A, Yamashita TE, et al. Natural history of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viremia after seroconversion and proximal to AIDS in a large cohort of homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 2000;181:872–80. - PubMed
-
- Mellors JW, Munoz A, Giorgi JV, et al. Plasma viral load and CD4+ lymphocytes as prognostic markers of HIV-1 infection. Ann Intern Med. 1997;126:946–54. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita TE, Phair JP, Munoz A, et al. Immunologic and virologic response to highly active antiretroviral therapy in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. AIDS. 2001;15:735–46. - PubMed
-
- Sterling TR, Vlahov D, Astemborski J, et al. Initial plasma HIV-1 RNA levels and progression to AIDS in women and men. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:720–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI 31834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD 32632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI052065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 42590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR 00083/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 34989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000083/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 34994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 35004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR 00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 34993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

