Decreased expression of beta1- and beta2-adrenoceptors in human diabetic atrial appendage
- PMID: 12857355
- PMCID: PMC203305
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-2-6
Decreased expression of beta1- and beta2-adrenoceptors in human diabetic atrial appendage
Abstract
Background: Using the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model, we have recently showed that the expression and function of beta1-adrenoreceptor were decreased in the diabetic rat heart. However, the effect of diabetes on expression of beta-adrenoreceptors in human cardiac tissue remains undefined. Therefore, the focus of the present study was to investigate the effect of diabetes on mRNA encoding beta1- and beta2-ARs in human atrial tissues.
Methods: Right atrial appendages from five diabetic (mean age 65 +/- 4.5; 4 female, 1 male) and five nondiabetic patients (mean age 56.2 +/- 2.8; 4 male, 1 female) undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting were collected and assayed using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for their mRNA content. No patient from these two groups suffered from acute myocardial infarction and/or failure. All diabetic patients received insulin for at least two years and had been diagnosed as diabetics for at least five years.
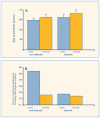
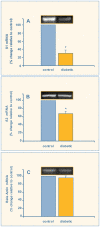
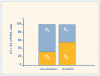
Results: When compared with levels in nondiabetics, steady state levels of mRNA encoding beta1-adrenoreceptor decreased by 69.2 +/- 7.6% in diabetic patients while beta2-adrenoreceptor mRNA decreased by 32.2 +/- 5.5% (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Our findings show a decreased expression of beta1- and beta2-adrenoreceptors in human diabetic atrial appendage.
Figures
References
-
- Rodrigues B, McNeill JH. The diabetic heart: metabolic causes for the development of a cardiomyopathy. Cardiovas Res. 1992;26:913–922. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz RJ, Rockman HA, Koch WJ. Catecholamines, cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors, and heart failure. Circulation. 2000;101:1634–7. - PubMed
-
- Fein FS, Aronson RS, Nordin C, Miller-Green B, Sonnenblick EH. Altered myocardial response to ouabain in diabetic rats: mechanics and electro physiology. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1983;15:769–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

