Mycotoxins
- PMID: 12857779
- PMCID: PMC164220
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.16.3.497-516.2003
Mycotoxins
Abstract
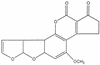
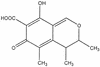
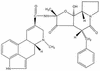
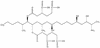
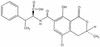
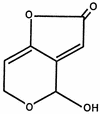
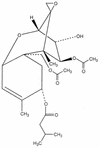
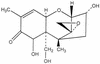
Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites produced by microfungi that are capable of causing disease and death in humans and other animals. Because of their pharmacological activity, some mycotoxins or mycotoxin derivatives have found use as antibiotics, growth promotants, and other kinds of drugs; still others have been implicated as chemical warfare agents. This review focuses on the most important ones associated with human and veterinary diseases, including aflatoxin, citrinin, ergot akaloids, fumonisins, ochratoxin A, patulin, trichothecenes, and zearalenone.
Figures
References
-
- Abramson, D., E. Usleber, and E. Marlbauer. 2001. Immunochemical method for citrinin. p. 195-204. In M. W. Trucksess and A. F. Pohland (ed.), Mycotoxin protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, N.J. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics. 1998. Toxic effects of indoor molds. Pediatrics 101:712-714. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, S. J. 1995. Compositional changes in surface mycoflora during ripening of naturally fermented sausages. J. Food Protect. 58:426-429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources