ROCK and nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent activation of cyclooxygenase-2 by Rho GTPases: effects on tumor growth and therapeutic consequences
- PMID: 12857884
- PMCID: PMC165696
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-01-0016
ROCK and nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent activation of cyclooxygenase-2 by Rho GTPases: effects on tumor growth and therapeutic consequences
Abstract
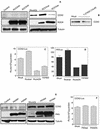
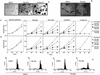
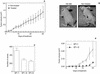
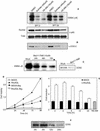
Rho GTPases are overexpressed in a variety of human tumors contributing to both tumor proliferation and metastasis. Recently, several studies demonstrate an essential role of transcriptional regulation in Rho GTPases-induced oncogenesis. Herein, we demonstrate that RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 promote the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) at the transcriptional level by a mechanism that is dependent on the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), but not Stat3, a transcription factor required for RhoA-induced tumorigenesis. With respect to RhoA, this effect is dependent on ROCK, but not PKN. Treatment of RhoA-, Rac1-, and Cdc42-transformed epithelial cells with Sulindac and NS-398, two well-characterized nonsteroid antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), results in growth inhibition as determined by cell proliferation assays. Accordingly, tumor growth of RhoA-expressing epithelial cells in syngeneic mice is strongly inhibited by NS-398 treatment. The effect of NSAIDs over RhoA-induced tumor growth is not exclusively dependent on COX-2 because DNA-binding of NF-kappaB is also abolished upon NSAIDs treatment, resulting in complete loss of COX-2 expression. Finally, treatment of RhoA-transformed cells with Bay11-7083, a specific NF-kappaB inhibitor, leads to inhibition of cell proliferation. We suggest that treatment of human tumors that overexpress Rho GTPases with NSAIDs and drugs that target NF-kappaB could constitute a valid antitumoral strategy.
Figures



References
-
- Aznar, S., and Lacal, J.C. (2001a). Rho signals to cell growth and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 165, 1-10. - PubMed
-
- Aznar, S., and Lacal, J.C. (2001b). Searching new targets for anticancer drug design: the families of Ras and RhoGTPases and their effectors. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 67, 193-234. - PubMed
-
- Aznar, S., and Lacal, J.C. (2003). Rho GTPases in human carcinogenesis: a tale of excess. Rev. Oncol. (in press).
-
- Bar-Sagi, D., and Hall, A. (2000). Ras and Rho GTPases: a family reunion. Cell 103, 227-238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

