Exogenous interleukin-12 protects against lethal infection with coxsackievirus B4
- PMID: 12857896
- PMCID: PMC165221
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.15.8272-8279.2003
Exogenous interleukin-12 protects against lethal infection with coxsackievirus B4
Abstract
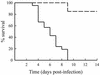
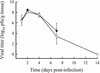
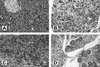
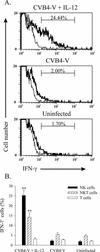
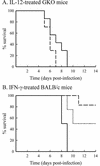
Infections with the group B coxsackieviruses either can be asymptomatic or can lead to debilitating chronic diseases. To elucidate the mechanism by which these viruses cause chronic disease, we developed a mouse model of chronic pancreatitis by using a virulent variant of coxsackievirus B4, CVB4-V. Infection with CVB4-V results in an early, severe pancreatitis, which can lead to mortality or progress to chronic pancreatitis. Chronic pancreatitis, in this model, is due to immunopathological mechanisms. We investigated whether interleukin-12 (IL-12) could modulate the outcome of CVB4-V infection. Eighty-five percent of the infected mice treated with 500 ng of IL-12 survived, whereas all untreated mice succumbed. To understand the mechanism underlying the beneficial effect of IL-12, we investigated the role of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma). Three lines of evidence suggest that the protective effect of IL-12 is due to IFN-gamma. First, administration of IL-12 increased the production of endogenous IFN-gamma in CVB4-V-infected mice. Both NK and NKT cells were identified as the source of IFN-gamma. Second, IFN-gamma knockout mice treated with IL-12 succumbed to infection with CVB4-V. Third, wild-type mice treated with IFN-gamma survived infection with CVB4-V. Due to the antiviral effects of IFN-gamma, we examined whether IL-12 treatment affected viral replication. Administration of IL-12 did not decrease viral replication in the pancreas, but it did prevent extensive tissue damage and the subsequent development of chronic pancreatitis. The data suggest that IL-12 treatment during CVB4-V infection is able to suppress the immunopathological mechanisms that lead to chronic disease.
Figures


References
-
- Atkins, M. B., M. J. Robertson, M. Gordon, M. T. Lotze, M. DeCoste, J. S. DuBois, J. Ritz, A. B. Sandler, H. D. Edington, P. D. Garzone, J. W. Mier, C. M. Canning, L. Battiato, H. Tahara, and M. L. Sherman. 1997. Phase I evaluation of intravenous recombinant human interleukin 12 in patients with advanced malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 3:409-417. - PubMed
-
- Babcock, G. F., and S. E. Frede. 1998. Intracellular cytokines, p. 9.9.1-9.9.10. In J. P. Robinson, Z. Darzynkiewicz, P. N. Dean, A. R. Hibbs, A. Orfao, P. S. Rabinovitch, and L. L. Wheeless (ed.), Current protocols in cytometry, vol. 2. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Biron, C. A., and J. S. Orange. 1995. IL-12 in acute viral infectious disease. Res. Immunol. 146:590-600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

