Pathogenic effects of human herpesvirus 6 in human lymphoid tissue ex vivo
- PMID: 12857897
- PMCID: PMC165251
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.15.8280-8289.2003
Pathogenic effects of human herpesvirus 6 in human lymphoid tissue ex vivo
Abstract
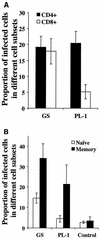
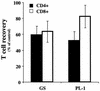
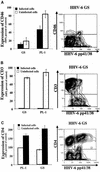
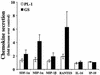
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) is a potentially immunosuppressive agent that has been suggested to act as a cofactor in the progression of human immunodeficiency virus disease. However, the lack of suitable experimental models has hampered the elucidation of the mechanisms of HHV-6-mediated immune suppression. Here, we used ex vivo lymphoid tissue to investigate the cellular tropism and pathogenic mechanisms of HHV-6. Viral strains belonging to both HHV-6 subgroups (A and B) were able to productively infect human tonsil tissue fragments in the absence of exogenous stimulation. The majority of viral antigen-expressing cells were CD4(+) T lymphocytes expressing a nonnaive phenotype, while CD8(+) T cells were efficiently infected only with HHV-6A. Accordingly, HHV-6A infection resulted in the depletion of both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells, whereas in HHV-6B-infected tissue CD4(+) T cells were predominantly depleted. The expression of different cellular antigens was dramatically altered in HHV-6-infected tissues: whereas CD4 was upregulated, both CD46, which serves as a cellular receptor for HHV-6, and CD3 were downmodulated. However, CD3 downmodulation was restricted to infected cells, while the loss of CD46 expression was generalized. Moreover, HHV-6 infection markedly enhanced the production of the CC chemokine RANTES, whereas other cytokines and chemokines were only marginally affected. These results provide the first evidence, in a physiologically relevant study model, that HHV-6 can severely affect the physiology of secondary lymphoid organs through direct infection of T lymphocytes and modulation of key membrane receptors and chemokines.
Figures

References
-
- Berger, E. A., P. M. Murphy, and J. M. Farber. 1999. Chemokine receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: roles in viral entry, tropism, and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:657-700. - PubMed
-
- Challoner, P. B., K. T Smith, J. D. Parker, D. L. MacLeod, S. N. Coulter, T. M. Rose, E. R. Schultz, L. Bennett, R. L. Garber, M. Chang, P. A. Schad, P. M. Stewart, R. C. Nowinski, J. P. Brown, and G. C. Burmer. 1995. Plaque-associated expression of human herpesvirus 6 in multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:7440-7444. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Glushakova, S., B. Baibakov, L. B. Margolis, and J. Zimmerberg. 1995. Infection of human tonsil histocultures: a model for HIV pathogenesis. Nat. Med. 1:1320-1322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

