Overexpression of the alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase in MDCK cells increases influenza virus sensitivity to neuraminidase inhibitors
- PMID: 12857911
- PMCID: PMC165236
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.15.8418-8425.2003
Overexpression of the alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase in MDCK cells increases influenza virus sensitivity to neuraminidase inhibitors
Abstract
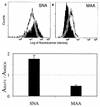
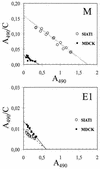
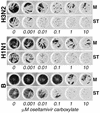
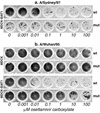
No reliable cell culture assay is currently available for monitoring human influenza virus sensitivity to neuraminidase inhibitors (NAI). This can be explained by the observation that because of a low concentration of sialyl-alpha2,6-galactose (Sia[alpha2,6]Gal)-containing virus receptors in conventional cell lines, replication of human virus isolates shows little dependency on viral neuraminidase. To test whether overexpression of Sia(alpha2,6)Gal moieties in cultured cells could make them suitable for testing human influenza virus sensitivity to NAI, we stably transfected MDCK cells with cDNA of human 2,6-sialyltransferase (SIAT1). Transfected cells expressed twofold-higher amounts of 6-linked sialic acids and twofold-lower amounts of 3-linked sialic acids than parent MDCK cells as judged by staining with Sambucus nigra agglutinin and Maackia amurensis agglutinin, respectively. After transfection, binding of a clinical human influenza virus isolate was increased, whereas binding of its egg-adapted variant which preferentially bound 3-linked receptors was decreased. The sensitivity of human influenza A and B viruses to the neuraminidase inhibitor oseltamivir carboxylate was substantially improved in the SIAT1-transfected cell line and was consistent with their sensitivity in neuraminidase enzyme assay and with the hemagglutinin (HA) receptor-binding phenotype. MDCK cells stably transfected with SIAT1 may therefore be a suitable system for testing influenza virus sensitivity to NAI.
Figures
References
-
- Abed, Y., A. M. Bourgault, R. J. Fenton, P. J. Morley, D. Gower, I. J. Owens, M. Tisdale, and G. Boivin. 2002. Characterization of 2 influenza A(H3N2) clinical isolates with reduced susceptibility to neuraminidase inhibitors due to mutations in the hemagglutinin gene. J. Infect. Dis. 186:1074-1080. - PubMed
-
- Air, G. M., and W. G. Laver. 1989. The neuraminidase of influenza virus. Proteins 6:341-356. - PubMed
-
- Barnett, J. M., A. Cadman, D. Gor, M. Dempsey, M. Walters, A. Candlin, M. Tisdale, P. J. Morley, I. J. Owens, R. J. Fenton, A. P. Lewis, E. C. Claas, G. F. Rimmelzwaan, R. De Groot, and A. D. Osterhaus. 2000. Zanamivir susceptibility monitoring and characterization of influenza virus clinical isolates obtained during phase II clinical efficacy studies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:78-87. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baum, L. G., and J. C. Paulson. 1990. Sialyloligosaccharides of the respiratory epithelium in the selection of human influenza virus receptor specificity. Acta Histochem. Suppl. 40:35-38. - PubMed
-
- Boorsma, D. M., and J. G. Streefkerk. 1979. Periodate or glutaraldehyde for preparing peroxidase conjugates? J. Immunol. Methods 30:245-255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

