In vivo dynamics of antigen-specific regulatory T cells not predicted from behavior in vitro
- PMID: 12857946
- PMCID: PMC166408
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1533365100
In vivo dynamics of antigen-specific regulatory T cells not predicted from behavior in vitro
Abstract
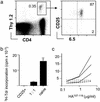
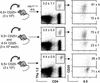
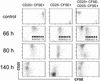
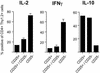
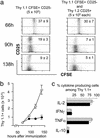
Adoptive transfer of antigen-specific CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells was used to analyze the stability of their phenotype, their behavior after immunization, and their mode of suppressing cotransferred naive T cells in vivo. We found that regulatory T cells maintained their phenotype in the absence of antigen, were not anergic in vivo, and proliferated as extensively as naive CD4+ T cells after immunization without losing their suppressive function in vivo and in vitro. In vivo, the expansion of cotransferred naive T cells was suppressed relatively late in the response such that regulatory T cells expressing mostly IL-10 but not IL-2 or IFN-gamma represented the dominant subset of cells. Our results reveal properties of regulatory T cells that were not predicted from in vitro studies.
Figures

References
-
- Modigliani, Y., Bandeira, A. & Coutinho, A. (1996) Immunol. Rev. 149, 155–120. - PubMed
-
- Le Douarin, N., Corbel, C., Bandeira, A., Thomas-Vaslin, V., Modigliani, Y., Coutinho, A. & Salaun, J. (1996) Immunol. Rev. 149, 35–53. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi, S., Sakaguchi, N., Shimizu, J., Yamazaki, S., Sakihama, T., Itoh, M., Kuniyasu, Y., Nomura, T., Toda, M. & Takahashi, T. (2001) Immunol. Rev. 182, 18–32. - PubMed
-
- Jordan, M. S., Riley, M. P., von Boehmer, H. & Caton, A. J. (2000) Eur. J. Immunol. 30, 136–144. - PubMed
-
- Jordan, M. S., Boesteanu, A., Reed, A. J., Petrone, A. L., Holenbeck, A. E., Lerman, M. A., Naji, A. & Caton, A. J. (2001) Nat. Immunol. 2, 301–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

