Mammalian transcription factor LSF is a target of ERK signaling
- PMID: 12858339
- PMCID: PMC3403288
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.10549
Mammalian transcription factor LSF is a target of ERK signaling
Abstract
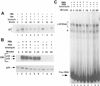
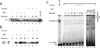
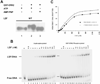
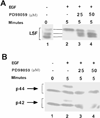
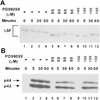
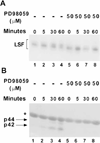
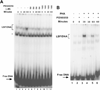
LSF is a mammalian transcription factor that is rapidly and quantitatively phosphorylated upon growth induction of resting, peripheral human T cells, as assayed by a reduction in its electrophoretic mobility. The DNA-binding activity of LSF in primary T cells is greatly increased after this phosphorylation event (Volker et al. [1997]: Genes Dev 11:1435-1446). We demonstrate here that LSF is also rapidly and quantitatively phosphorylated upon growth induction in NIH 3T3 cells, although its DNA-binding activity is not significantly altered. Three lines of experimentation established that ERK is responsible for phosphorylating LSF upon growth induction in both cell types. First, phosphorylation of LSF by ERK is sufficient to cause the reduced electrophoretic mobility of LSF. Second, the amount of ERK activity correlates with the extent of LSF phosphorylation in both primary human T cells and NIH 3T3 cells. Finally, specific inhibitors of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway inhibit LSF modification in vivo. This phosphorylation by ERK is not sufficient for activation of LSF DNA-binding activity, as evidenced both in vitro and in mouse fibroblasts. Nonetheless, activation of ERK is a prerequisite for the substantial increase in LSF DNA-binding activity upon activation of resting T cells, indicating that ERK phosphorylation is necessary but not sufficient for activation of LSF in this cell type.
Copyright 2003 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitogenic stimulation of resting T cells causes rapid phosphorylation of the transcription factor LSF and increased DNA-binding activity.Genes Dev. 1997 Jun 1;11(11):1435-46. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.11.1435. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9192871
-
Pharmacologic mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors interact synergistically with STI571 to induce apoptosis in Bcr/Abl-expressing human leukemia cells.Cancer Res. 2002 Jan 1;62(1):188-99. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11782377
-
Interferon-alpha2b reduces phosphorylation and activity of MEK and ERK through a Ras/Raf-independent mechanism.Br J Cancer. 2000 Aug;83(4):532-8. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1263. Br J Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10945503 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide activation of the MEK-ERK1/2 pathway in human monocytic cells mediates tissue factor and tumor necrosis factor alpha expression by inducing Elk-1 phosphorylation and Egr-1 expression.Blood. 2001 Sep 1;98(5):1429-39. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.5.1429. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11520792
-
Lineage-specific and ubiquitous biological roles of the mammalian transcription factor LSF.Gene. 2004 Dec 8;343(1):23-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.08.010. Gene. 2004. PMID: 15563829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate LSF occupancy at the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter.J Virol. 2005 May;79(10):5952-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.10.5952-5962.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15857981 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the g1/s transition in hepatocytes: involvement of the cyclin-dependent kinase cdk1 in the DNA replication.Int J Hepatol. 2012;2012:689324. doi: 10.1155/2012/689324. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Int J Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 23091735 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors LSF and E2Fs: tandem cyclists driving G0 to S?Cell Cycle. 2009 Jul 15;8(14):2146-51. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.14.9089. Epub 2009 Jul 21. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19556876 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor LSF (TFCP2) inhibits melanoma growth.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 19;7(3):2379-90. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6230. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26506241 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of deregulated Notch signaling and Ras pathway in human hepatocarcinogenesis.J Mol Histol. 2011 Oct;42(5):473-81. doi: 10.1007/s10735-011-9353-3. Epub 2011 Sep 3. J Mol Histol. 2011. PMID: 21892768
References
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen- activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Bing Z, Reddy SAG, Ren Y, Qin J, Liao WS-L. Purification and characterization of the serum amyloid A3 enhancer factor. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:24649–24656. - PubMed
-
- Bruni P, Minopoli G, Brancaccio T, Napolitano M, Faraonio R, Zambrano N, Hansen U, Russo T. Fe65, a ligand of the Alzheimer's β-amyloid precursor protein, blocks cell cycle progression by downregulating thymidylate synthase expression. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:35481–35488. - PubMed
-
- Casolaro V, Keane-Myers AM, Swendeman SL, Steindler C, Zhong F, Sheffery M, Georas SN, Ono SJ. Identification and characterization of a critical CP2-binding element in the human interleukin-4 promoter. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:36605–36611. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Karin M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature. 2001;410:37–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

