Normal values of B type natriuretic peptide in infants, children, and adolescents
- PMID: 12860862
- PMCID: PMC1767791
- DOI: 10.1136/heart.89.8.875
Normal values of B type natriuretic peptide in infants, children, and adolescents
Abstract
Objective: To determine normal values of plasma B type natriuretic peptide from infancy to adolescence using a commercially available rapid assay.
Setting: Tertiary referral centre.
Design: The study was cross sectional. Plasma BNP concentration was measured in 195 healthy infants, children, and adolescents from birth to 17.6 years using the triage BNP assay (a fluorescence immunoassay).
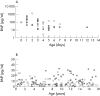
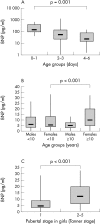
Results: During the first week of life, the mean (SD) plasma concentration of BNP in newborn infants decreased significantly from 231.6 (197.5) to 48.4 (49.1) pg/ml (p = 0.001). In all subjects older than two weeks plasma BNP concentration was less than 32.7 pg/ml. There was no significant difference in mean plasma BNP measured in boys and girls younger than 10 years (8.3 (6.9) v 8.5 (7.5) pg/ml). In contrast, plasma concentration of BNP in girls aged 10 years or older was significantly higher than in boys of the same age group (12.1 (9.6) v 5.1 (3.5) pg/ml, p < 0.001). Plasma BNP concentrations were higher in pubertal than in prepubertal girls (14.4 (9.7) v 7.1 (6.6) pg/ml, p < 0.001) and were correlated with the Tanner stage (r = 0.41, p = 0.001).
Conclusions: Plasma BNP concentrations in newborn infants are relatively high, vary greatly, and decrease rapidly during the first week of life. In children older than 2 weeks, the mean plasma concentration of BNP is lower than in adults. There is a sex related difference in the second decade of life, with higher BNP concentrations in girls. BNP concentrations in girls are related to pubertal stage.
Figures
References
-
- Levin ER, Gardner DG, Samson WK. Natriuretic peptides. N Engl J Med 1998;339:321–8. - PubMed
-
- Yoshimura M, Yasue H, Okamura, et al. Different secretion pattern of atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 1993;87:464–9. - PubMed
-
- Yandle TG. Biochemistry of natriuretic peptides. J Intern Med 1994;235:561–76. - PubMed
-
- Maeda K, Takayoshi T, Wada A, et al. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide as a biochemical marker of high left ventricular end-diastolic pressure in patients with symptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. Am Heart J 1998;135:825–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
