Exercise-induced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA in rat skeletal muscle is dependent on fibre type
- PMID: 12860922
- PMCID: PMC2343332
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.043026
Exercise-induced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA in rat skeletal muscle is dependent on fibre type
Abstract
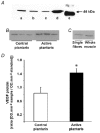
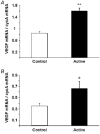
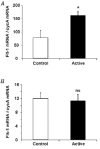
In this study, we quantified the expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene in individual muscle fibres at the end of a single 90 min run of 20-25 m min-1, at 10 % incline. In addition, we evaluated the co-ordinated expression of several hypoxia-sensitive genes, including the ORP-150 gene. Individual fibres were taken from rat plantaris muscle, either at the end of a single bout of exercise or at rest, and classified as Type I, IIa, IIx or IIb, according to the expression of myosin heavy chain (MHC) isoforms. VEGF mRNA levels increased by 90 % in exercising whole plantaris in comparison with those in control muscle (P < 0.001), while the VEGF protein content increased by 72 % (P < 0.05). Using real-time PCR analysis, an accurate and reproducible method for quantification of mRNA levels, a marked rise in VEGF transcript levels was observed at the end of exercise in individual myofibres (P < 0.05), providing the first direct evidence that VEGF transcripts increase in muscle cells after a single bout of exercise. This exercise-induced increase in VEGF transcript levels was specifically observed in type IIb myofibres, which are predominantly glycolytic and more susceptible to local hypoxia than oxidative myofibres such as type I or IIa fibres (110 %, P < 0.05). Moreover, treadmill exercise increased the expression of two hypoxia-sensitive genes. The levels of mRNA for Flt-1, a VEGF-specific receptor, and those for ORP-150, a chaperone essential for the secretion of mature VEGF, increased in whole plantaris muscles (108 and 92 %, respectively, P < 0.05). Taken together, these findings are consistent with the suggestion that hypoxia could be one of the mechanisms involved in exercise-induced capillary growth.
Figures
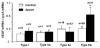
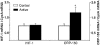
References
-
- Agbulut O, Li Z, Mouly V, Buttler-Browne GS. Analysis of skeletal and cardiac muscle from desmin knock-out and normal mice by high resolution separation of myosin heavy-chain isoforms. Biol Cell. 1996;88:131–135. - PubMed
-
- Amaral SL, Papanek PE, Greene AS. Angiotensin II and VEGF are involved in angiogenesis induced by short-term exercise training. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001;281:H1163–1169. - PubMed
-
- Andersen P. Capillary density in skeletal muscle of man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975;95:203–205. - PubMed
-
- Annex BH, Torgan CE, Lin P, Taylor DA, Thompson MA, Peters KG, Kraus WE. Induction and maintenance of increased VEGF protein by chronic motor nerve stimulation in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:H860–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

