OX40 (CD134) controls memory T helper 2 cells that drive lung inflammation
- PMID: 12860930
- PMCID: PMC2194076
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021937
OX40 (CD134) controls memory T helper 2 cells that drive lung inflammation
Abstract
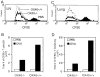
Asthma is caused by memory Th2 cells that often arise early in life and persist after repeated encounters with allergen. Although much is known regarding how Th2 cells develop, there is little information about the molecules that regulate memory Th2 cells after they have formed. Here we show that the costimulatory molecule OX40 is expressed on memory CD4 cells. In already sensitized animals, blocking OX40-OX40L interactions at the time of inhalation of aerosolized antigen suppressed memory effector accumulation in lung draining lymph nodes and lung, and prevented eosinophilia, airway hyperreactivity, mucus secretion, and Th2 cyto-kine production. Demonstrating that OX40 signals directly regulate memory T cells, antigen-experienced OX40-deficient T cells were found to divide initially but could not survive and accumulate in large numbers after antigen rechallenge. Thus, OX40-OX40L interactions are pivotal to the efficiency of recall responses regulated by memory Th2 cells.
Figures
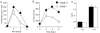

Similar articles
-
Development of allergic inflammation in a murine model of asthma is dependent on the costimulatory receptor OX40.J Exp Med. 2001 Feb 5;193(3):387-92. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.3.387. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11157058 Free PMC article.
-
OX40 blockade inhibits house dust mite driven allergic lung inflammation in mice and in vitro allergic responses in humans.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Apr;45(4):1116-28. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445163. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25545270
-
Constitutive OX40/OX40 ligand interaction induces autoimmune-like diseases.J Immunol. 2002 Oct 15;169(8):4628-36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.8.4628. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12370402
-
OX40-OX40 ligand interaction in T-cell-mediated immunity and immunopathology.Adv Immunol. 2010;105:63-98. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(10)05003-0. Adv Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20510730 Review.
-
Epigenetic and Transcriptional Regulation in the Induction, Maintenance, Heterogeneity, and Recall-Response of Effector and Memory Th2 Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 12;9:2929. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02929. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30619290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neutralization of TSLP inhibits airway remodeling in a murine model of allergic asthma induced by chronic exposure to house dust mite.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e51268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051268. Epub 2013 Jan 2. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23300949 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory drugs suppress Th1-inducing ability of dendritic cells but enhance Th2-mediated allergic responses.Blood Adv. 2020 Aug 11;4(15):3572-3585. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019001410. Blood Adv. 2020. PMID: 32761232 Free PMC article.
-
CD137 as an Attractive T Cell Co-Stimulatory Target in the TNFRSF for Immuno-Oncology Drug Development.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 11;13(10):2288. doi: 10.3390/cancers13102288. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34064598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OX40 costimulation turns off Foxp3+ Tregs.Blood. 2007 Oct 1;110(7):2501-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-070748. Epub 2007 Jun 15. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17575071 Free PMC article.
-
The Host Peritoneal Cavity Harbors Prominent Memory Th2 and Early Recall Responses to an Intestinal Nematode.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 28;13:842870. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.842870. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35418979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wills-Karp, M. 1999. Immunologic basis of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:255–281. - PubMed
-
- Umetsu, D.T., J.J. McIntire, O. Akbari, C. Macaubas, and R.H. DeKruyff. 2002. Asthma: an apidemic of dysregulated immunity. Nat. Immunol. 3:715–720. - PubMed
-
- Croft, M., L.M. Bradley, and S.L. Swain. 1994. Naive versus memory CD4 T cell response to antigen. Memory cells are less dependent on accessory cell costimulation and can respond to many antigen-presenting cell types including resting B cells. J. Immunol. 152:2675–2685. - PubMed
-
- Byrne, J.A., J.L. Butler, and M.D. Cooper. 1988. Differential activation requirements for virgin and memory T cells. J. Immunol. 141:3249–3257. - PubMed
-
- Luqman, M., and K. Bottomly. Activation requirements for CD4+ T cells differing in CD45R expression. J. Immunol. 149:2300–2306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

