OX40 (CD134) controls memory T helper 2 cells that drive lung inflammation
- PMID: 12860930
- PMCID: PMC2194076
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021937
OX40 (CD134) controls memory T helper 2 cells that drive lung inflammation
Abstract
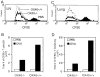
Asthma is caused by memory Th2 cells that often arise early in life and persist after repeated encounters with allergen. Although much is known regarding how Th2 cells develop, there is little information about the molecules that regulate memory Th2 cells after they have formed. Here we show that the costimulatory molecule OX40 is expressed on memory CD4 cells. In already sensitized animals, blocking OX40-OX40L interactions at the time of inhalation of aerosolized antigen suppressed memory effector accumulation in lung draining lymph nodes and lung, and prevented eosinophilia, airway hyperreactivity, mucus secretion, and Th2 cyto-kine production. Demonstrating that OX40 signals directly regulate memory T cells, antigen-experienced OX40-deficient T cells were found to divide initially but could not survive and accumulate in large numbers after antigen rechallenge. Thus, OX40-OX40L interactions are pivotal to the efficiency of recall responses regulated by memory Th2 cells.
Figures
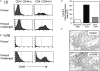
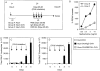
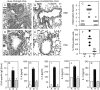
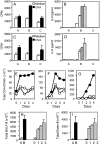
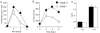
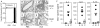

References
-
- Wills-Karp, M. 1999. Immunologic basis of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:255–281. - PubMed
-
- Umetsu, D.T., J.J. McIntire, O. Akbari, C. Macaubas, and R.H. DeKruyff. 2002. Asthma: an apidemic of dysregulated immunity. Nat. Immunol. 3:715–720. - PubMed
-
- Croft, M., L.M. Bradley, and S.L. Swain. 1994. Naive versus memory CD4 T cell response to antigen. Memory cells are less dependent on accessory cell costimulation and can respond to many antigen-presenting cell types including resting B cells. J. Immunol. 152:2675–2685. - PubMed
-
- Byrne, J.A., J.L. Butler, and M.D. Cooper. 1988. Differential activation requirements for virgin and memory T cells. J. Immunol. 141:3249–3257. - PubMed
-
- Luqman, M., and K. Bottomly. Activation requirements for CD4+ T cells differing in CD45R expression. J. Immunol. 149:2300–2306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

