Mutation in fas ligand impairs maturation of thymocytes bearing moderate affinity T cell receptors
- PMID: 12860933
- PMCID: PMC2194074
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030220
Mutation in fas ligand impairs maturation of thymocytes bearing moderate affinity T cell receptors
Abstract
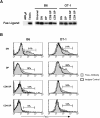
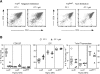
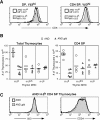
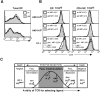
Fas ligand, best known as a death-inducer, is also a costimulatory molecule required for maximal proliferation of mature antigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. We now extend the role of Fas ligand by showing that it can also influence thymocyte development. T cell maturation in some, but not all, strains of TCR transgenic mice is severely impaired in thymocytes expressing mutant Fas ligand incapable of interacting with Fas. Mutant Fas ligand inhibits neither negative selection nor death by neglect. Instead, it appears to modulate positive selection of thymocytes expressing both class I- and class II-restricted T cell receptors of moderate affinity for their positively selecting ligands. Fas ligand is therefore an inducer of death, a costimulator of peripheral T cell activation, and an accessory molecule in positive selection.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impaired peripheral deletion of activated T cells in mice lacking the common cytokine receptor gamma-chain: defective Fas ligand expression in gamma-chain-deficient mice.J Immunol. 1997 Nov 15;159(10):4737-44. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9366397
-
T cells expressing receptors of different affinity for antigen ligands reveal a unique role for p59fyn in T cell development and optimal stimulation of T cells by antigen.J Immunol. 1998 Jun 1;160(11):5410-9. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9605142
-
Altered thymocyte development resulting from expressing a deleting ligand on selecting thymic epithelium.J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):2988-95. J Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1578126
-
Influence of the affinity of selecting ligands on T cell positive and negative selection and the functional maturity of the positively selected T cells.Crit Rev Immunol. 1997;17(5-6):399-410. Crit Rev Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9419427 Review.
-
Cross-talk between the T cell antigen receptor and the glucocorticoid receptor regulates thymocyte development.Stem Cells. 1996 Sep;14(5):490-500. doi: 10.1002/stem.140490. Stem Cells. 1996. PMID: 8888490 Review.
Cited by
-
Reverse Signaling of Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily Proteins in Macrophages and Microglia: Superfamily Portrait in the Neuroimmune Interface.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 19;10:262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00262. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30838001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro- and anti-apoptotic CD95 signaling in T cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2011 Apr 8;9:7. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-9-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2011. PMID: 21477291 Free PMC article.
-
Collapse of the tumor stroma is triggered by IL-12 induction of Fas.Mol Ther. 2013 Jul;21(7):1369-77. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.58. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Mol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23568260 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and the roles it plays in homeostatic and degenerative processes within the central nervous system.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;7(1):42-59. doi: 10.1007/s11481-011-9287-2. Epub 2011 Jul 5. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21728035 Review.
-
GATA-3 regulates the homeostasis and activation of CD8+ T cells.J Immunol. 2013 Jan 1;190(1):428-37. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201361. Epub 2012 Dec 5. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23225883 Free PMC article.
References
-
- von Boehmer, H. 1994. Positive selection of lymphocytes. Cell. 76:219–228. - PubMed
-
- Jameson, S.C., K.A. Hogquist, and M.J. Bevan. 1995. Positive selection of thymocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13:93–125. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey, D.I., and A. Zlotnik. 1993. Control points in early T-cell development. Immunol. Today. 14:547–553. - PubMed
-
- von Boehmer, H., and H.J. Fehling. 1997. Structure and function of the pre-T cell receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15:433–452. - PubMed
-
- Nossal, G.J.V. 1994. Negative selection of lymphocytes. Cell. 76:229–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

