Downregulation of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor expression inhibits Erk signalling with concomitant suppression of invasiveness due to loss of uPAR-beta1 integrin complex in colon cancer cells
- PMID: 12865932
- PMCID: PMC2394266
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601098
Downregulation of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor expression inhibits Erk signalling with concomitant suppression of invasiveness due to loss of uPAR-beta1 integrin complex in colon cancer cells
Abstract
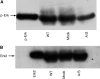
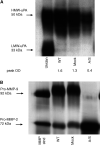
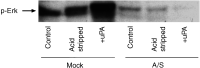
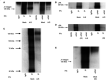
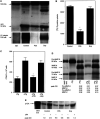
Cancer invasion is regulated by cell surface proteinases and adhesion molecules. Interaction between specific cell surface molecules such as urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and integrins is crucial for tumour invasion and metastasis. In this study, we examined whether uPAR and beta1 integrin form a functional complex to mediate signalling required for tumour invasion. We assessed the expression of uPAR/beta1 integrin complex, Erk signalling pathway, adhesion, uPA and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression, migration/invasion and matrix degradation in a colon cancer cell line in which uPAR expression was modified. Antisense inhibition of the cell surface expression of uPAR by 50% in human colon carcinoma HCT116 cells (A/S) suppressed Erk-MAP kinase activity by two-fold. Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor antisense treatment of HCT116 cells was associated with a 1.3-fold inhibition of adhesion, approximately four-fold suppression of HMW-uPA secretion and inhibition of pro-MMP-9 secretion. At a functional level, uPAR antisense resulted in a four-fold decline in migration/invasion and abatement of plasmin-mediated matrix degradation. In empty vector-transfected cells (mock), uPA strongly elevated basal Erk activation. In contrast, in A/S cells, uPA induction of Erk activation was not observed. Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor associated with beta1 integrin in mock-transfected cells. Disruption of uPAR-beta1 integrin complex in mock-transfected cells with a specific peptide (P25) inhibited uPA-mediated Erk-MAP kinase pathway and inhibited migration/invasion and plasmin-dependent matrix degradation through suppression of pro-MMP-9/MMP-2 expression. This novel paradigm of uPAR-integrin signalling may afford opportunities for alternative therapeutic strategies for the treatment of cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Aguirre Ghiso JA, Alonso DF, Farias EF, Gomez DE, de Kier Joffe EB (1999a) Deregulation of the signaling pathways controlling urokinase-production. Its relationship with the invasive phenotype. Eur J Biochem 263: 295–304 - PubMed
-
- Ahmed N, Niu J, Dorahy DJ, Gu X, Andrews S, Meldrum CJ, Scott RJ, Baker MS, Macreadie IG, Agrez MV (2002a) Direct integrin alphavbeta6-ERK binding: implications for tumour growth. Oncogene 21: 1370–1380 - PubMed
-
- Ahmed N, Pansino F, Baker M, Rice G, Quinn M (2002b) Association between [alpha]v[beta]6 integrin expression, elevated p42/44 kDa MAPK, and plasminogen-dependent matrix degradation in ovarian cancer. J Cell Biochem 84: 675–686 - PubMed
-
- Ahmed N, Pansino F, Clyde R, Murthi P, Quinn MA, Rice GE, Agrez MV, Mok S, Baker MS (2002c) Overexpression of alphavbeta6 integrin in serous epithelial ovarian cancer regulates extracellular matrix degradation via the plasminogen activation cascade. Carcinogenesis 23: 237–244 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

