Arginine residues in the active site of human phenol sulfotransferase (SULT1A1)
- PMID: 12867416
- PMCID: PMC3118444
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M306045200
Arginine residues in the active site of human phenol sulfotransferase (SULT1A1)
Abstract
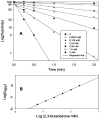
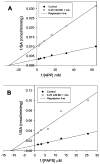
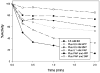
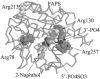
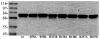
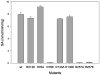
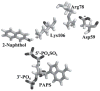
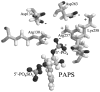
Cytosolic sulfotransferases (STs) catalyze the sulfation of hydroxyl containing compounds. Human phenol sulfotransferase (SULT1A1) is the major human ST that catalyzes the sulfation of simple phenols. Because of its broad substrate specificity and lack of endogenous substrates, the biological function of SULT1A1 is believed to be an important detoxification enzyme. In this report, amino acid modification, computer structure modeling, and site-directed mutagenesis were used for studies of Arg residues in the active site of SULT1A1. The Arg-specific modification reagent, 2,3-butanedione, inactivated SULT1A1 in an efficient, time- and concentration-dependent manner, suggesting Arg residues play an important role in the catalytic activity of SULT1A1. According to the computer model, Arg78, Arg130, and Arg257 may be important for SULT1A1 catalytic activity. Site-directed mutagenesis results demonstrated that the positive charge on Arg78 is not critical for SULT1A1 because R78A is still active. In contrast, a negative charge at this position, R78E, completely inactivated SULT1A1. Arg78 is in close proximity to the site of sulfuryl group transfer. Arg257 is located very close to the 3'-phosphate in adenosine 3'-phosphate 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS). Site-directed mutagenesis demonstrated that Arg257 is critical for SULT1A1: both R257A and R257E are inactive. Although Arg130 is also located very close to the 3'-phosphate of PAPS, R130A and R130E are still active, suggesting that Arg130 is not a critical residue for the catalytic activity of SULT1A1. Computer modeling suggests that the ionic interaction between the positive charge on Arg257, and the negative charge on 3'-phosphate is the primary force stabilizing the specific binding of PAPS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Carboxyl residues in the active site of human phenol sulfotransferase (SULT1A1).Biochemistry. 2000 Dec 26;39(51):16000-7. doi: 10.1021/bi0021479. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 11123927
-
Crystal structure-based studies of cytosolic sulfotransferase.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2001;15(2):67-75. doi: 10.1002/jbt.1. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2001. PMID: 11284047 Review.
-
Isotope exchange at equilibrium indicates a steady state ordered kinetic mechanism for human sulfotransferase.Biochemistry. 2008 Nov 11;47(45):11894-9. doi: 10.1021/bi801211t. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18928301 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine residues in human phenol sulfotransferases.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Apr 1;67(7):1355-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2003.12.007. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15013851
-
Design and Interpretation of Human Sulfotransferase 1A1 Assays.Drug Metab Dispos. 2016 Apr;44(4):481-4. doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.068205. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016. PMID: 26658224 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genistein induction of human sulfotransferases in HepG2 and Caco-2 cells.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008 Dec;103(6):553-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2008.00316.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18715236 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Sulfotransferase Induction Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 Proliferation.Biomed J Sci Tech Res. 2019;22(5):16960-16967. doi: 10.26717/bjstr.2019.22.003812. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Biomed J Sci Tech Res. 2019. PMID: 36312461 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfation of catecholamines and serotonin by SULT1A3 allozymes.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 May;151:104-113. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29524394 Free PMC article.
-
Redox regulation of human estrogen sulfotransferase (hSULT1E1).Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 May 1;73(9):1474-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.12.026. Epub 2006 Dec 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17266938 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfation of dietary flavonoids by human sulfotransferases.Xenobiotica. 2009 Apr;39(4):312-22. doi: 10.1080/00498250802714915. Xenobiotica. 2009. PMID: 19350454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weinshilboum R, Aksoy I. Chem Biol Interact. 1994;92:233–246. - PubMed
-
- Varin L, Marsolais F, Richard M, Rouleau M. FASEB J. 1997;11:517–525. - PubMed
-
- Sakakibara Y, Takami Y, Nakayama T, Suiko M, Liu C. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:6242–6247. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y, Bergold A, Duffel MW. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:30313–30319. - PubMed
-
- Marsolais F, Varin L. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:30458–30463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

