YjdE (AdiC) is the arginine:agmatine antiporter essential for arginine-dependent acid resistance in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 12867448
- PMCID: PMC165756
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.15.4402-4409.2003
YjdE (AdiC) is the arginine:agmatine antiporter essential for arginine-dependent acid resistance in Escherichia coli
Abstract
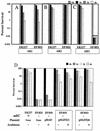
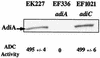
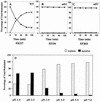
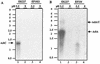
To survive in extremely acidic conditions, Escherichia coli has evolved three adaptive acid resistance strategies thought to maintain internal pH. While the mechanism behind acid resistance system 1 remains enigmatic, systems 2 and 3 are known to require external glutamate (system 2) and arginine (system 3) to function. These latter systems employ specific amino acid decarboxylases and putative antiporters that exchange the extracellular amino acid substrate for the intracellular by-product of decarboxylation. Although GadC is the predicted antiporter for system 2, the antiporter specific for arginine/agmatine exchange has not been identified. A computer-based homology search revealed that the yjdE (now called adiC) gene product shared an overall amino acid identity of 22% with GadC. A series of adiC mutants isolated by random mutagenesis and by targeted deletion were shown to be defective in arginine-dependent acid resistance. This defect was restored upon introduction of an adiC(+)-containing plasmid. An adiC mutant proved incapable of exchanging extracellular arginine for intracellular agmatine but maintained wild-type levels of arginine decarboxylase protein and activity. Western blot analysis indicated AdiC is an integral membrane protein. These data indicate that the arginine-to-agmatine conversion defect of adiC mutants was at the level of transport. The adi gene region was shown to be organized into two transcriptional units, adiAY and adiC, which are coordinately regulated but independently transcribed. The data also illustrate that the AdiA decarboxylase:AdiC antiporter system is designed to function only at acid levels sufficient to harm the cell.
Figures



References
-
- Auger, E. A., K. E. Redding, T. Plumb, L. C. Childs, S.-Y. Meng, and G. N. Bennett. 1989. Construction of lac fusions to the inducible arginine and lysine decarboxylase genes of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol. Microbiol. 3:609-620. - PubMed
-
- Bocker, E. A., and E. E. Snell. 1972. Amino acid decarboxylases, p. 217-253. In P. Boyer (ed.), The enzymes, vol. 6. Academic Press, New York, N.Y.
-
- Castanie-Cornet, M. P., and J. W. Foster. 2001. Escherichia coli acid resistance: cAMP receptor protein and a 20-bp cis-acting sequence control pH and stationary phase expression of the gadA and gadBC glutamate decarboxylase genes. Microbiology 147:709-715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

