The glycosyltransferase domain of penicillin-binding protein 2a from Streptococcus pneumoniae catalyzes the polymerization of murein glycan chains
- PMID: 12867450
- PMCID: PMC165775
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.15.4418-4423.2003
The glycosyltransferase domain of penicillin-binding protein 2a from Streptococcus pneumoniae catalyzes the polymerization of murein glycan chains
Abstract
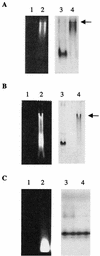
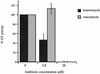
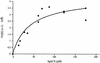
The bacterial peptidoglycan consists of glycan chains of repeating beta-1,4-linked N-acetylglucosaminyl-N-acetylmuramyl units cross-linked through short peptide chains. The polymerization of the glycans, or glycosyltransfer (GT), and transpeptidation (TP) are catalyzed by bifunctional penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). The beta-lactam antibiotics inhibit the TP reaction, but their widespread use led to the development of drug resistance in pathogenic bacteria. In this context, the GT catalytic domain represents a potential target in the antibacterial fight. In this work, the in vitro polymerization of glycan chains by the extracellular region of recombinant Streptococcus pneumoniae PBP2a, namely, PBP2a* (the asterisk indicates the soluble form of the protein) is presented. Dansylated lipid II was used as the substrate, and the kinetic parameters K(m) and k(cat)/K(m) were measured at 40.6 micro M (+/- 15.5) and 1 x 10(-3) M(-1) s(-1), respectively. The GT reaction catalyzed by PBP2a* was inhibited by moenomycin and vancomycin. Furthermore, the sequence between Lys 78 and Ser 156 is required for enzymatic activity, whereas it is dispensable for lipid II binding. In addition, we confirmed that this region of the protein is also involved in membrane interaction, independently of the transmembrane anchor. The characterization of the catalytically active GT domain of S. pneumoniae PBP2a may contribute to the development of new inhibitors, which are urgently needed to renew the antibiotic arsenal.
Figures


References
-
- Di Guilmi, A. M., A. Dessen, O. Dideberg, and T. Vernet. 2002. Bifunctional penicillin-binding proteins: focus on the glycosyltransferase domain and its specific inhibitor moenomycin. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 3:63-75. - PubMed
-
- Di Guilmi, A. M., N. Mouz, J. P. Andrieu, J. Hoskins, S. R. Jaskunas, J. Gagnon, O. Dideberg, and T. Vernet. 1998. Identification, purification, and characterization of transpeptidase and glycosyltransferase domains of Streptococcus pneumoniae penicillin-binding protein 1a. J. Bacteriol. 180:5652-5659. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

