Analysis of the interaction between the transcription factor sigmaG and the anti-sigma factor SpoIIAB of Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 12867473
- PMCID: PMC165760
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.15.4615-4619.2003
Analysis of the interaction between the transcription factor sigmaG and the anti-sigma factor SpoIIAB of Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
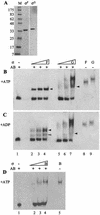
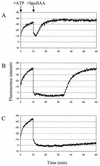
The activation of sigma(G), a transcription factor, in Bacillus subtilis is coupled to the completion of engulfment during sporulation. SpoIIAB, an anti-sigma factor involved in regulation of sigma(F), is also shown to form a complex with sigma(G) in vitro. SpoIIAA, the corresponding anti-anti-sigma factor, can disrupt the SpoIIAB:sigma(G) complex, releasing free sigma(G). The data suggest the existence of an as-yet-unknown mechanism to keep sigma(G) inactive prior to engulfment.
Figures
References
-
- Alper, S., L. Duncan, and R. Losick. 1994. An adenosine nucleotide switch controlling the activity of a cell type-specific transcription factor in B. subtilis. Cell 77:195-205. - PubMed
-
- Campbell, E. A., S. Masuda, J. L. Sun, O. Muzzin, C. A. Olson, S. Wang, and S. A. Darst. 2002. Crystal structure of the Bacillus stearothermophilus anti-sigma factor SpoIIAB with the sporulation sigma factor σF. Cell 108:795-807. - PubMed
-
- Diederich, B., J. F. Wilkinson, T. Magnin, M. Najafi, J. Errington, and M. D. Yudkin. 1994. Role of interactions between SpoIIAA and SpoIIAB in regulating cell-specific transcription factor σF of Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 8:2653-2663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

