Comparative genomic analysis reveals independent expansion of a lineage-specific gene family in vertebrates: the class II cytokine receptors and their ligands in mammals and fish
- PMID: 12869211
- PMCID: PMC179897
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-4-29
Comparative genomic analysis reveals independent expansion of a lineage-specific gene family in vertebrates: the class II cytokine receptors and their ligands in mammals and fish
Abstract
Background: The high degree of sequence conservation between coding regions in fish and mammals can be exploited to identify genes in mammalian genomes by comparison with the sequence of similar genes in fish. Conversely, experimentally characterized mammalian genes may be used to annotate fish genomes. However, gene families that escape this principle include the rapidly diverging cytokines that regulate the immune system, and their receptors. A classic example is the class II helical cytokines (HCII) including type I, type II and lambda interferons, IL10 related cytokines (IL10, IL19, IL20, IL22, IL24 and IL26) and their receptors (HCRII). Despite the report of a near complete pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) genome sequence, these genes remain undescribed in fish.
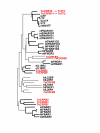
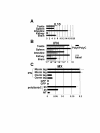
Results: We have used an original strategy based both on conserved amino acid sequence and gene structure to identify HCII and HCRII in the genome of another pufferfish, Tetraodon nigroviridis that is amenable to laboratory experiments. The 15 genes that were identified are highly divergent and include a single interferon molecule, three IL10 related cytokines and their potential receptors together with two Tissue Factor (TF). Some of these genes form tandem clusters on the Tetraodon genome. Their expression pattern was determined in different tissues. Most importantly, Tetraodon interferon was identified and we show that the recombinant protein can induce antiviral MX gene expression in Tetraodon primary kidney cells. Similar results were obtained in Zebrafish which has 7 MX genes.
Conclusion: We propose a scheme for the evolution of HCII and their receptors during the radiation of bony vertebrates and suggest that the diversification that played an important role in the fine-tuning of the ancestral mechanism for host defense against infections probably followed different pathways in amniotes and fish.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phylogeny and evolution of class-I helical cytokines.J Endocrinol. 2006 Apr;189(1):1-25. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06591. J Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16614377 Review.
-
The interferon system of teleost fish.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006 Feb;20(2):172-91. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2005.01.010. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006. PMID: 15939626 Review.
-
Fox gene loci in Takifugu rubripes and Tetraodon nigroviridis genomes and comparison with those of medaka and zebrafish genomes.Genome. 2011 Dec;54(12):965-72. doi: 10.1139/g11-065. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Genome. 2011. PMID: 22073989
-
Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of an IL-21 homologue from Tetraodon nigroviridis.Cytokine. 2006 Aug;35(3-4):126-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2006.07.010. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Cytokine. 2006. PMID: 16987670
-
Genomic characterization and expression analysis of the first nonmammalian renin genes from zebrafish and pufferfish.Physiol Genomics. 2004 Feb 13;16(3):314-22. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00012.2003. Physiol Genomics. 2004. PMID: 14645735
Cited by
-
Genetic resistance to rhabdovirus infection in teleost fish is paralleled to the derived cell resistance status.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33935. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033935. Epub 2012 Apr 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22514610 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish-based platform for emerging bio-contaminants and virus inactivation research.Sci Total Environ. 2023 May 10;872:162197. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162197. Epub 2023 Feb 11. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36781138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimating the tempo and mode of gene family evolution from comparative genomic data.Genome Res. 2005 Aug;15(8):1153-60. doi: 10.1101/gr.3567505. Genome Res. 2005. PMID: 16077014 Free PMC article.
-
A possible anticancer agent, type III interferon, activates cell death pathways and produces antitumor effects.Clin Dev Immunol. 2011;2011:479013. doi: 10.1155/2011/479013. Epub 2011 Oct 16. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22013482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-26, a Cytokine With Roles in Extracellular DNA-Induced Inflammation and Microbial Defense.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 12;10:204. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00204. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30809226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aparicio S, Chapman J, Stupka E, Putnam N, Chia JM, Dehal P, Christoffels A, Rash S, Hoon S, Smit A, Gelpke MD, Roach J, Oh T, Ho IY, Wong M, Detter C, Verhoef F, Predki P, Tay A, Lucas S, Richardson P, Smith SF, Clark MS, Edwards YJ, Doggett N, Zharkikh A, Tavtigian SV, Pruss D, Barnstead M, Evans C, Baden H, Powell J, Glusman G, Rowen L, Hood L, Tan YH, Elgar G, Hawkins T, Venkatesh B, Rokhsar D, Brenner S. Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science. 2002;297:1301–1310. doi: 10.1126/science.1072104. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dehal P, Satou Y, Campbell RK, Chapman J, Degnan B, De Tomaso A, Davidson B, Di Gregorio A, Gelpke M, Goodstein DM, Harafuji N, Hastings KE, Ho I, Hotta K, Huang W, Kawashima T, Lemaire P, Martinez D, Meinertzhagen IA, Necula S, Nonaka M, Putnam N, Rash S, Saiga H, Satake M, Terry A, Yamada L, Wang HG, Awazu S, Azumi K, Boore J, Branno M, Chin-Bow S, DeSantis R, Doyle S, Francino P, Keys DN, Haga S, Hayashi H, Hino K, Imai KS, Inaba K, Kano S, Kobayashi K, Kobayashi M, Lee BI, Makabe KW, Manohar C, Matassi G, Medina M, Mochizuki Y, Mount S, Morishita T, Miura S, Nakayama A, Nishizaka S, Nomoto H, Ohta F, Oishi K, Rigoutsos I, Sano M, Sasaki A, Sasakura Y, Shoguchi E, Shin-i T, Spagnuolo A, Stainier D, Suzuki MM, Tassy O, Takatori N, Tokuoka M, Yagi K, Yoshizaki F, Wada S, Zhang C, Hyatt PD, Larimer F, Detter C, Doggett N, Glavina T, Hawkins T, Richardson P, Lucas S, Kohara Y, Levine M, Satoh N, Rokhsar DS. The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: insights into chordate and vertebrate origins. Science. 2002;298:2157–2167. doi: 10.1126/science.1080049. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murphy PM. Molecular mimicry and the generation of host defense protein diversity. Cell. 1993;72:823–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

