The loss of TGF-beta signaling promotes prostate cancer metastasis
- PMID: 12869309
- PMCID: PMC1502411
- DOI: 10.1016/S1476-5586(03)80058-1
The loss of TGF-beta signaling promotes prostate cancer metastasis
Abstract
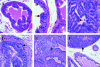
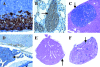
In breast and colon cancers, transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta signaling initially has an antineoplastic effect, inhibiting tumor growth, but eventually exerts a proneoplastic effect, increasing motility and cancer spread. In prostate cancer, studies using human samples have correlated the loss of the TGF-beta type II receptor (T beta R II) with higher tumor grade. To determine the effect of an inhibited TGF-beta pathway on prostate cancer, we bred transgenic mice expressing the tumorigenic SV40 large T antigen in the prostate with transgenic mice expressing a dominant negative T beta R II mutant (DN II R) in the prostate. Transgene(s) and TGF-beta 1 expression were identified in the prostate and decreased protein levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor type I, as a marker for TGF-beta signaling, correlated with expression of the DN II R. Although the sizes of the neoplastic prostates were not enlarged, increased amounts of metastasis were observed in mice expressing both transgenes compared to age-matched control mice expressing only the large T antigen transgene. Our study demonstrates for the first time that a disruption of TGF-beta signaling in prostate cancer plays a causal role in promoting tumor metastasis.
Figures




References
-
- Ohori M, Goad JR, Wheeler TM, Eastham JA, Thompson TC, Scardino PT. Can radical prostatectomy alter the progression of poorly differentiated prostate cancer? J Urol. 1994;152:1843–1849. - PubMed
-
- Quinn DI, Henshall SM, Head DR, Golovsky D, Wilson JD, Brenner PC, Turner JJ, Delprado W, Finlayson JF, Stricker PD, Grygiel JJ, Sutherland RL. Prognostic significance of p53 nuclear accumulation in localized prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1585–1594. - PubMed
-
- Kim IY, Ahn HJ, Lang S, Oefelein MG, Oyasu R, Kozlowski JM, Lee C. Loss of expression of transforming growth factor-beta receptors is associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 1998;4:1625–1630. - PubMed
-
- Guo Y, Jacobs SC, Kyprianou N. Down-regulation of protein and mRNA expression for transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta1) type I and type II receptors in human prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 1997;71:573–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

