Integrated mapping, chromosomal sequencing and sequence analysis of Cryptosporidium parvum
- PMID: 12869580
- PMCID: PMC403770
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.1555203
Integrated mapping, chromosomal sequencing and sequence analysis of Cryptosporidium parvum
Erratum in
- Genome Res. 2004 Feb;14(2):327
Abstract
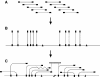
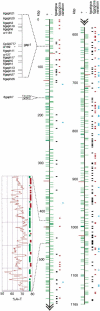
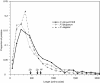
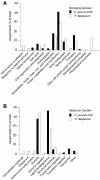
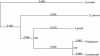
The apicomplexan Cryptosporidium parvum is one of the most prevalent protozoan parasites of humans. We report the physical mapping of the genome of the Iowa isolate, sequencing and analysis of chromosome 6, and approximately 0.9 Mbp of sequence sampled from the remainder of the genome. To construct a robust physical map, we devised a novel and general strategy, enabling accurate placement of clones regardless of clone artefacts. Analysis reveals a compact genome, unusually rich in membrane proteins. As in Plasmodium falciparum, the mean size of the predicted proteins is larger than that in other sequenced eukaryotes. We find several predicted proteins of interest as potential therapeutic targets, including one exhibiting similarity to the chloroquine resistance protein of Plasmodium. Coding sequence analysis argues against the conventional phylogenetic position of Cryptosporidium and supports an earlier suggestion that this genus arose from an early branching within the Apicomplexa. In agreement with this, we find no significant synteny and surprisingly little protein similarity with Plasmodium. Finally, we find two unusual and abundant repeats throughout the genome. Among sequenced genomes, one motif is abundant only in C. parvum, whereas the other is shared with (but has previously gone unnoticed in) all known genomes of the Coccidia and Haemosporida. These motifs appear to be unique in their structure, distribution and sequences.
Figures


References
-
- Apweiler, R., Attwood, T.K., Bairoch, A., Bateman, A., Birney, E., Biswas, M., Bucher, P., Cerutti, L., Corpet, F., Croning, M.D., et al. 2000. InterPro—An integrated documentation resource for protein families, domains and functional sites. Bioinformatics 16: 1145-1150. - PubMed
-
- Armson, A., Meloni, B.P., Reynoldson, J.A., and Thompson, R.C.A. 1999. Assessment of drugs against Cryptosporidium parvum using a simple in vitro screening method. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 178: 227-233. - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
-
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/taxonomyhome.html/; NCBI Taxonomy Homepage.
-
- http://www.sanger.ac.uk/Projects/E_tenella/; The Sanger Institute Eimeria tenella Genome Project.
-
- http://www.tigr.org/tdb/e2k1/tga1/; The TIGR Toxoplasma gondii Genome Project.
-
- http://mips.gsf.de/cgi-bin/proj/medgen/mitofilter; MITOP—Description of MITOP.
-
- http://gecco.org.chemie.uni-frankfurt.de/pats/pats-index.ph; Modlab—The Molecular Design Laboratory.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
