Regulated recruitment of HP1 to a euchromatic gene induces mitotically heritable, epigenetic gene silencing: a mammalian cell culture model of gene variegation
- PMID: 12869583
- PMCID: PMC196232
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1102803
Regulated recruitment of HP1 to a euchromatic gene induces mitotically heritable, epigenetic gene silencing: a mammalian cell culture model of gene variegation
Abstract
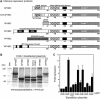
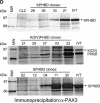
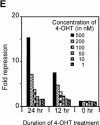
Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) is a key component of constitutive heterochromatin in Drosophila and is required for stable epigenetic gene silencing classically observed as position effect variegation. Less is known of the family of mammalian HP1 proteins, which may be euchromatic, targeted to expressed loci by repressor-corepressor complexes, and retained there by Lys 9-methylated histone H3 (H3-MeK9). To characterize the physical properties of euchromatic loci bound by HP1, we developed a strategy for regulated recruitment of HP1 to an expressed transgene in mammalian cells by using a synthetic, hormone-regulated KRAB repression domain. We show that its obligate corepressor, KAP1, can coordinate all the machinery required for stable gene silencing. In the presence of hormone, the transgene is rapidly silenced, spatially recruited to HP1-rich nuclear regions, assumes a compact chromatin structure, and is physically associated with KAP1, HP1, and the H3 Lys 9-specific methyltransferase, SETDB1, over a highly localized region centered around the promoter. Remarkably, silencing established by a short pulse of hormone is stably maintained for >50 population doublings in the absence of hormone in clonal-cell populations, and the silent transgenes in these clones show promoter hypermethylation. Thus, like variegation in Drosophila, recruitment of mammalian HP1 to a euchromatic promoter can establish a silenced state that is epigenetically heritable.
Figures


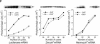


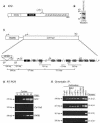
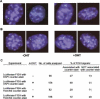

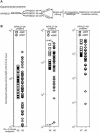
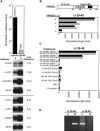

Comment in
-
Heterochromatin: stable and unstable invasions at home and abroad.Genes Dev. 2003 Aug 1;17(15):1805-12. doi: 10.1101/gad.1123303. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12897049 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ayyanathan K., Fredericks, W.J., Berking, C., Herlyn, M., Balakrishnan, C., Gunther, E., and Rauscher III, F.J. 2000. Hormone-dependent tumor regression in vivo by an inducible transcriptional repressor directed at the PAX3-FKHR oncogene. Cancer Res. 60: 5803-5814. - PubMed
-
- Baker W.K. 1968. Position-effect variegation. Adv. Genet. 14: 133-169. - PubMed
-
- Bannister A.J., Zegerman, P., Partridge, J.F., Miska, E.A., Thomas, J.O., Allshire, R.C., and Kouzarides, T. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120-124. - PubMed
-
- Cameron E.E., Bachman, K.E., Myohanen, S., Herman, J.G., and Baylin, S.B. 1999. Synergy of demethylation and histone deacetylase inhibition in the re-expression of genes silenced in cancer. Nat. Genet. 21: 103-107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI53237/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA09171/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI41136/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA010815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA10815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM64691/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA095620/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA095561/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AI053237/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA92088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009171/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 CA095620/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI041136/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095561/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI52742/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI041136/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064691/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
