Chlamydomonas reinhardtii selenocysteine tRNA[Ser]Sec
- PMID: 12869703
- PMCID: PMC1370458
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.5510503
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii selenocysteine tRNA[Ser]Sec
Abstract
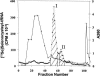
Eukaryotic selenocysteine (Sec) protein insertion machinery was thought to be restricted to animals, but the occurrence of both Sec-containing proteins and the Sec insertion system was recently found in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a member of the plant kingdom. Herein, we used RT-PCR to determine the sequence of C. reinhardtii Sec tRNA[Ser]Sec, the first non-animal eukaryotic Sec tRNA[Ser]Sec sequence. Like its animal counterpart, it is 90 nucleotides in length, is aminoacylated with serine by seryl-tRNA synthetase, and decodes specifically UGA. Evolutionary analyses of known Sec tRNAs identify the C. reinhardtii form as the most diverged eukaryotic Sec tRNA[Ser]Sec and reveal a common origin for this tRNA in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Selenocysteine synthesis in mammalia: an identity switch from tRNA(Ser) to tRNA(Sec).J Mol Biol. 1996 Oct 18;263(1):8-19. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0552. J Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8890909
-
Selenocysteine tRNA and serine tRNA are aminoacylated by the same synthetase, but may manifest different identities with respect to the long extra arm.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994 Dec;315(2):293-301. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1503. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994. PMID: 7986071
-
Selenoproteins and selenocysteine insertion system in the model plant cell system, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.EMBO J. 2002 Jul 15;21(14):3681-93. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf372. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12110581 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of selenocysteine, the 21st amino acid in the genetic code, and a novel pathway for cysteine biosynthesis.Adv Nutr. 2011 Mar;2(2):122-8. doi: 10.3945/an.110.000265. Epub 2011 Mar 10. Adv Nutr. 2011. PMID: 22332041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenocysteine inserting tRNAs: an overview.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1999 Jun;23(3):335-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1999.tb00403.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10371037 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomics of Volvocine Algae.Adv Bot Res. 2012;64:185-243. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391499-6.00006-2. Adv Bot Res. 2012. PMID: 25883411 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudouridine-guide RNAs and other Cbf5p-associated RNAs in Euglena gracilis.RNA. 2004 Jul;10(7):1034-46. doi: 10.1261/rna.7300804. RNA. 2004. PMID: 15208440 Free PMC article.
-
Steady-state levels of imported tRNAs in Chlamydomonas mitochondria are correlated with both cytosolic and mitochondrial codon usages.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(5):1521-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn1073. Epub 2009 Jan 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19139073 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH-dependent and -independent disulfide reductase systems.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 Nov 1;127:248-261. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.03.051. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 29609022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of selenium utilization traits.Genome Biol. 2005;6(8):R66. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-8-r66. Epub 2005 Jul 27. Genome Biol. 2005. PMID: 16086848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amberg, R., Mizutani, T., Wu, X.Q., and Gross, H.J. 1996. Selenocysteine synthesis in mammalia: an identity switch from tRNA(Ser) to tRNA(Sec). J. Mol. Biol. 263: 8–19. - PubMed
-
- Böck, A., Forchhammer, K., Heider, J., and Baron, C. 1991. Selenoprotein synthesis: an expansion of the genetic code. Trends Biochem. Sci. 16: 463–467. - PubMed
-
- Diamond, A., Dudock, B., and Hatfield, D. 1981. Structure and properties of a bovine liver UGA suppressor serine tRNA with a tryptophan anticodon. Cell 25: 497–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
