Tityustoxin-K(alpha) blockade of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3
- PMID: 12871837
- PMCID: PMC1573937
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705343
Tityustoxin-K(alpha) blockade of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3
Abstract
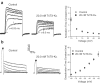
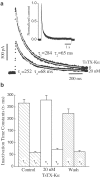
1. We investigated the action of TsTX-Kalpha on cloned Kv1.3 channels of the Shaker subfamily of voltage-gated potassium channels, using the voltage-clamp technique. Highly purified TsTX-Kalpha was obtained from the venom of the Brazilian scorpion Tityus serrulatus using a new purification protocol. Our results show that TsTX-Kalpha blocks Kv1.3 with high affinity in two expression systems. 2. TsTX-Kalpha blockade of Kv1.3 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes was found to be completely reversible and to exhibit a pH dependence. The K(D) was 3.9 nM at pH 7.5, 9.5 nM at pH 7.0 and 94.5 nM at pH 6.5. 3. The blocking properties of TsTX-Kalpha in a mammalian cell line (L929), stably transfected to express Kv1.3, were studied using the patch-clamp technique. In this preparation, the toxin had a K(D) of 19.8 nM at pH 7.4. 4. TsTX-Kalpha was found to affect neither the voltage-dependence of activation, nor the activation and deactivation time constants. The block appeared to be independent of the transmembrane voltage and the toxin did not interfere with the C-type inactivation process. 5. Taken as a whole, our findings indicate that TsTX-Kalpha acts as a simple blocker of Kv1.3 channels. It is concluded that this toxin is a useful tool for probing not only the physiological roles of Kv1.2, but also those mediated by Kv1.3 channels.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Toxin and subunit specificity of blocking affinity of three peptide toxins for heteromultimeric, voltage-gated potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Jun;285(3):1051-60. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998. PMID: 9618407
-
Tityustoxin-K alpha, a structurally novel and highly potent K+ channel peptide toxin, interacts with the alpha-dendrotoxin binding site on the cloned Kv1.2 K+ channel.Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;44(2):430-6. Mol Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8355670
-
The 'functional' dyad of scorpion toxin Pi1 is not itself a prerequisite for toxin binding to the voltage-gated Kv1.2 potassium channels.Biochem J. 2004 Jan 1;377(Pt 1):25-36. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030115. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 12962541 Free PMC article.
-
Potassium channels as therapeutic targets for autoimmune disorders.Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2003 Sep;6(5):640-7. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2003. PMID: 14579513 Review.
-
Chimeras of KcsA and Kv1 as a bioengineering tool to study voltage-gated potassium channels and their ligands.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Aug;190:114646. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114646. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34090876 Review.
Cited by
-
Developing a comparative docking protocol for the prediction of peptide selectivity profiles: investigation of potassium channel toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2012 Feb;4(2):110-38. doi: 10.3390/toxins4020110. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 22474570 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular mechanisms and behavioral consequences of Kv1.2 regulation in the rat cerebellum.J Neurosci. 2012 Jul 4;32(27):9228-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6504-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22764231 Free PMC article.
-
Variable threshold of trigeminal cold-thermosensitive neurons is determined by a balance between TRPM8 and Kv1 potassium channels.J Neurosci. 2009 Mar 11;29(10):3120-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4778-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19279249 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Brazilian scorpion venoms on the central nervous system.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2018 Jan 23;24:3. doi: 10.1186/s40409-018-0139-x. eCollection 2018. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29410679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and Chemical Synthesis of Cm39 (α-KTx 4.8): A Scorpion Toxin That Inhibits Voltage-Gated K+ Channel KV1.2 and Small- and Intermediate-Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels KCa2.2 and KCa3.1.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;15(1):41. doi: 10.3390/toxins15010041. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36668861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AIYAR J., WITHKA J.M., RIZZI J.P., SINGLETON D.H., ANDREWS G.C., LIN W., BOYD J., HANSON D.C., SIMON M., DETHLEFS B., LEE C.L., HALL J.E., GUTMAN G.A., CHANDY K.G. Topology of the pore-region of a K+ channel revealed by the NMR-derived structures of scorpion toxins. Neuron. 1995;15:1169–1181. - PubMed
-
- ARANTES E.C., PRADO W.A., SAMPAIO S.V., GIGLIO J.R. A simplified procedure for the fractionation of Tityus serrulatus venom: isolation and partial characterization of TsTX-IV, a new neurotoxin. Toxicon. 1989;27:907–916. - PubMed
-
- BLAUSTEIN M.P., ROGOWSKI R.S., SCHNEIDER M.J., KRUEGER B.K. Polypeptide toxins from the venoms of old world and new world scorpion preferentially block different potassium channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 1991;40:932–942. - PubMed
-
- COLEMAN S.K., NEWCOMBE J., PRYKE J., DOLLY J.O. Subunit composition of Kv1 channels in human CNS. J. Neurochem. 1999;73:849–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

