Antigen-dependent proliferation of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in vivo
- PMID: 12874258
- PMCID: PMC2194065
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030315
Antigen-dependent proliferation of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in vivo
Abstract
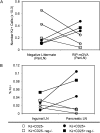
The failure of CD25+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) to proliferate after T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation in vitro has lead to their classification as naturally anergic. Here we use Tregs expressing a transgenic TCR to show that despite anergy in vitro, Tregs proliferate in response to immunization in vivo. Tregs also proliferate and accumulate locally in response to transgenically expressed tissue antigen whereas their CD25- counterparts are depleted at such sites. Collectively, these data suggest that the anergic state that characterizes CD25+ Tregs in vitro may not accurately reflect their responsiveness in vivo. These observations support a model in which Treg population dynamics are shaped by the local antigenic environment.
Figures



References
-
- Takahashi, T., Y. Kuniyasu, M. Toda, N. Sakaguchi, M. Itoh, M. Iwata, J. Shimizu, and S. Sakaguchi. 1998. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by CD25+ CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells: induction of autoimmune disease by breaking their anergic/suppressive state. Int. Immunol. 12:1969–1980. - PubMed
-
- Read, S., S. Mauze, C. Asseman, A. Bean, R. Coffman, and F. Powrie. 1998. CD38+ CD45RB(low) CD4+ T cells: a population of T cells with immune regulatory activities in vitro. Eur. J. Immunol. 28:3435–3447. - PubMed
-
- Suri-Payer, E., A.Z. Amar, A.M. Thornton, and E.M. Shevach. 1998. CD4+ CD25+ T cells inhibit both the induction and effector function of autoreactive T cells and represent a unique lineage of immunoregulatory cells. J. Immunol. 160:1212–1218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

