VH3 gene usage in neutralizing human antibodies specific for the Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc lectin heavy subunit
- PMID: 12874307
- PMCID: PMC166044
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4313-4319.2003
VH3 gene usage in neutralizing human antibodies specific for the Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc lectin heavy subunit
Abstract
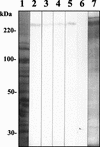
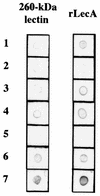
A combinatorial human immunoglobulin gene library was constructed from peripheral lymphocytes of an asymptomatic Entamoeba histolytica cyst passer and screened for the production of Fab antibody to the parasite. One of the Fab clones, CP33, recognized the 260-kDa galactose- and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (Gal/GalNAc)-specific lectin of E. histolytica. By shuffling the heavy and light chains of CP33 with the heavy and light chains of two libraries derived from the cyst passer and a liver abscess patient, 18 additional clones were obtained. Sequence analysis of the heavy-chain genes, including CP33-H, revealed that all the nearest V-segment germ lines belonged to the VH3 family (VH3-21, VH3-30, VH3-48, and VH3-53), but the levels of homology were only 85 to 95%. The closest D-segment germ line was D2-2 or D6-6, and for the J-segment the closest germ line was JH4b or JH6b. On the other hand, all the light-chain genes, including CP33-L, belonged to the V kappa 1 family, in which the closest V kappa germ line gene was 02/012 or L5, with the J kappa 1, J kappa 2, J kappa 4, or J kappa 5 segment. CP33 and three other Fabs obtained by light-chain shuffling were purified and analyzed further. All of these Fabs recognized the cysteine-rich domain of the 170-kDa heavy subunit of the Gal/GalNAc lectin. Preincubation of E. histolytica trophozoites with these Fabs significantly inhibited amebic adherence to Chinese hamster ovary cells and also inhibited erythrophagocytosis. The ability of the neutralizing antibodies to block erythrophagocytosis for the first time implicates the lectin in phagocytosis and VH3 antibodies in defense against parasitic infections. These results demonstrate the utility of a combinatorial human immunoglobulin gene library for identifying and characterizing neutralizing antibodies from humans with amebiasis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved affinity of a human anti-Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc lectin Fab fragment by a single amino acid modification of the light chain.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004 Nov;11(6):1085-8. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.11.6.1085-1088.2004. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15539510 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Entamoeba histolytica intermediate subunit lectin-specific human monoclonal antibodies generated in transgenic mice expressing human immunoglobulin loci.Infect Immun. 2009 Jan;77(1):549-56. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01002-08. Epub 2008 Nov 10. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19001071 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the 150-kDa surface antigen of Entamoeba histolytica as a galactose- and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable lectin.Parasitol Res. 1998 Aug;84(8):632-9. doi: 10.1007/s004360050462. Parasitol Res. 1998. PMID: 9747935
-
Entamoeba histolytica: from adherence to enteropathy.J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):420-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.420. J Infect Dis. 1989. PMID: 2536786 Review.
-
Structure and function of the Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc lectin.Int Rev Cytol. 2002;216:59-80. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(02)16003-7. Int Rev Cytol. 2002. PMID: 12049210 Review.
Cited by
-
Modification of a human monoclonal antibody Fab fragment specific for Plasmodium falciparum 19-kDa C-terminal merozoite surface protein 1 by site-directed mutagenesis.Parasitol Res. 2008 Jul;103(2):429-33. doi: 10.1007/s00436-008-0994-4. Epub 2008 Apr 30. Parasitol Res. 2008. PMID: 18446371
-
The anti-non-gal xenoantibody response to xenoantigens on gal knockout pig cells is encoded by a restricted number of germline progenitors.Am J Transplant. 2008 Sep;8(9):1829-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02337.x. Epub 2008 Jul 28. Am J Transplant. 2008. PMID: 18671678 Free PMC article.
-
Improved affinity of a human anti-Entamoeba histolytica Gal/GalNAc lectin Fab fragment by a single amino acid modification of the light chain.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004 Nov;11(6):1085-8. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.11.6.1085-1088.2004. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15539510 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-nonGal xenoantibody response to alpha1,3-galactosyltransferase gene knockout pig xenografts.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010 Apr;15(2):207-11. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e328336b854. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010. PMID: 20075731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody-Based Protective Immunity against Helminth Infections: Antibody Phage Display Derived Antibodies against BmR1 Antigen.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 22;18(11):2376. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112376. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29165352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abadi, J., J. Friedman, R. A. Mageed, R. Jefferis, M. C. Rodriguez-Barradas, and L. Pirofski. 1998. Human antibodies elicited by a pneumococcal vaccine express idiotypic determinants indicative of V(H)3 gene segment usage. J. Infect. Dis. 178:707-716. - PubMed
-
- Andris, J. S., P. H. Ehrlich, L. Ostberg, and J. D. Capra. 1992. Probing the human antibody repertoire to exogenous antigens. Characterization of the H and L chain V region gene segments from anti-hepatitis B virus antibodies. J. Immunol. 149:4053-4059. - PubMed
-
- Barbas, C. F., III, T. A. Collet, W. Amberg, P. Roben, J. M. Binley, D. Hoekstra, D. Cababa, T. M. Jones, R. A. Williamson, G. R. Pilkington, et al. 1993. Molecular profile of an antibody response to HIV-1 as probed by combinatorial libraries. J. Mol. Biol. 230:812-823. - PubMed
-
- Burchard, G. D., and R. Bilke. 1992. Adherence of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica strains to neutrophils. Parasitol. Res. 78:146-153. - PubMed
-
- Burton, D. R. 1995. Phage display. Immunotechnology 1:87-94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

