Pseudomonas aeruginosa slime glycolipoprotein is a potent stimulant of tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression and activation of transcription activators nuclear factor kappa B and activator protein 1 in human monocytes
- PMID: 12874341
- PMCID: PMC165984
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4614-4622.2003
Pseudomonas aeruginosa slime glycolipoprotein is a potent stimulant of tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression and activation of transcription activators nuclear factor kappa B and activator protein 1 in human monocytes
Abstract
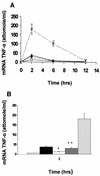
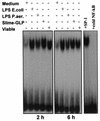
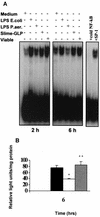
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, an opportunistic pathogen, causes infections associated with a high incidence of morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised hosts. Production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), primarily by cells of monocytic lineage, is a crucial event in the course of these infections. During in vivo infections with P. aeruginosa, both lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and extracellular slime glycolipoprotein (GLP) produced by mucoid and nonmucoid strains are released. In the present study, we sought to explore the relative contributions of these two bacterial products to TNF-alpha production by human monocytes. To this end, fresh human monocytes and THP-1 human monocytic cells were stimulated with P. aeruginosa LPS or GLP. GLP was found to be a more potent stimulus for TNF-alpha production (threefold higher) by human monocytes than LPS. Moreover, its effect was comparable to that of viable bacteria. Quantitative mRNA analysis revealed predominantly transcriptional regulation. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays and transfection assays demonstrated activation of NF-kappa B and activator protein 1 (AP-1). NF-kappa B activation by GLP was rapid and followed the same time course as that by viable bacteria, suggesting that bacteria could directly activate NF-kappa B through GLP. Moreover P. aeruginosa GLP induced the formation of AP-1 complex with delayed kinetics compared with NF-kappa B but much more efficiently than the homologous LPS. These results identify GLP as the most important stimulant for TNF-alpha production by human monocytes. Activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 by P. aeruginosa GLP may be involved not only in TNF-alpha induction but also in many of the inflammatory responses triggered in the course of infection with P. aeruginosa.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TNF-alpha induction by Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide or slime-glycolipoprotein in human monocytes is regulated at the level of Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase activity: a distinct role of Toll-like receptor 2 and 4.Scand J Immunol. 2008 Feb;67(2):193-203. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2007.02053.x. Epub 2007 Dec 12. Scand J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18086260
-
Interferon-gamma modulates the lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of AP-1 and NF-kappa B at the mRNA and protein level in human monocytes.Exp Hematol. 1996 Feb;24(2):228-35. Exp Hematol. 1996. PMID: 8641346
-
Inhibitory effect of E3330, a novel quinone derivative able to suppress tumor necrosis factor-alpha generation, on activation of nuclear factor-kappa B.Mol Pharmacol. 1996 May;49(5):860-73. Mol Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8622636
-
Hypothermia prolongs activation of NF-kappaB and augments generation of inflammatory cytokines.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Aug;287(2):C422-31. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00507.2003. Epub 2004 Apr 7. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15070815
-
Group B Streptococcus induces TNF-alpha gene expression and activation of the transcription factors NF-kappa B and activator protein-1 in human cord blood monocytes.J Immunol. 2000 Jul 1;165(1):419-25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.1.419. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10861080
Cited by
-
Interactions between human phagocytes and Candida albicans biofilms alone and in combination with antifungal agents.J Infect Dis. 2010 Jun 15;201(12):1941-9. doi: 10.1086/652783. J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20415537 Free PMC article.
-
Dampening Host Sensing and Avoiding Recognition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:852513. doi: 10.1155/2011/852513. Epub 2011 Jul 14. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21785567 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of immunomodulatory genes in human monocytes induced by voriconazole in the presence of Aspergillus fumigatus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Mar;51(3):1048-54. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01095-06. Epub 2006 Dec 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17178797 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic deletion of Sphk2 confers protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa mediated differential expression of genes related to virulent infection and inflammation in mouse lung.BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 16;20(1):984. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6367-9. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31842752 Free PMC article.
-
Participation of ATP7A in macrophage mediated oxidation of LDL.J Lipid Res. 2010 Jun;51(6):1471-7. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M003426. Epub 2009 Nov 23. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 19965596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arsenis, G., and G. Dimitracopoulos. 1986. Chemical composition of the extracellular slime glycolipoprotein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its relation to gentamicin resistance. J. Med. Microbiol. 21:199-202. - PubMed
-
- Banck, G., and A. Forsgren. 1999. Many bacterial species are mitogenic for human blood B lymphocytes. Scand. J. Immunol. 8:347-354. - PubMed
-
- Belcher, R., A. J. Nutten, and C. M. Sambrook. 1954. The determination of glycosamine. Analyst (London) 79:201-208.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

