The C terminus of YopT is crucial for activity and the N terminus is crucial for substrate binding
- PMID: 12874342
- PMCID: PMC166019
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4623-4632.2003
The C terminus of YopT is crucial for activity and the N terminus is crucial for substrate binding
Abstract
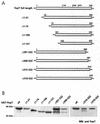
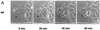
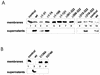
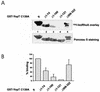
Recently, it was shown that Yersinia outer protein T (YopT) belongs to a new family of cysteine proteases containing invariant C, H, and D residues that are crucial for its activity. YopT cleaves RhoA, Rac, and Cdc42 at their C termini, thereby releasing them from the membrane. Moreover, YopT inhibits the Rho-rhotekin and Rho-guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor interactions. To characterize the active domain of YopT, we constructed N- and C-terminal truncations and expressed them as glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins in Escherichia coli. The toxin fragments were tested for stability by trypsin digestion. The activity of the proteins was studied by membrane release assay, rhotekin pulldown experiments, and microinjection. Whereas deletion of the first 74 N-terminal amino acids did not influence the activity of YopT, deletion of 8 amino acids from the C terminus led to complete loss of activity. N-terminal deletion of 100 amino acids led to an inactive protein, although it still contained the amino acids C139, H258, and D274, which are essential for catalysis. Loss of activity of the N-terminal deletions corresponded to the block of interaction with RhoA, indicating that residues 75 to 100 of YopT are essential for binding to the GTPase. By contrast, when up to 15 amino acids of the C terminus were deleted, the protein had no activity but was still able to interact with RhoA, suggesting a role for the C terminus in the enzyme activity of YopT.
Figures



References
-
- Aktories, K., G. Schmidt, and F. Hofmann. 2000. GTPases targeted by bacterial toxins, p. 311-331. In A. Hall (ed.), GTPases. Oxford University Press, Oxford, England.
-
- Barz, C., T. N. Abahji, K. Trülzsch, and J. Heesemann. 2000. The Yersinia Ser/Thr protein kinase YpkA/YopO directly interacts with the small GTPases RhoA and Rac-1. FEBS Lett. 482:139-143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

