Induction of antimicrobial pathways during early-phase immune response to Salmonella spp. in murine macrophages: gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and upregulation of IFN-gamma receptor alpha expression are required for NADPH phagocytic oxidase gp91-stimulated oxidative burst and control of virulent Salmonella spp
- PMID: 12874355
- PMCID: PMC166040
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4733-4741.2003
Induction of antimicrobial pathways during early-phase immune response to Salmonella spp. in murine macrophages: gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and upregulation of IFN-gamma receptor alpha expression are required for NADPH phagocytic oxidase gp91-stimulated oxidative burst and control of virulent Salmonella spp
Abstract
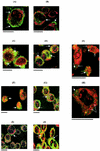
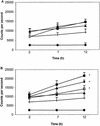
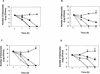
The effect of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) on elevation of reactive oxygen species and the viability of virulent wild-type and avirulent mutants of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and S. enterica serovar Infantis was studied in a murine macrophage cell line (J774.2 cells). S. enterica serovar Typhimurium 14028 phoP and a rough lipopolysaccharide mutant of S. enterica serovar Infantis 1326/28 (phi(r)) (avirulent mutants) induced NADPH phagocytic oxidase gp91 (gp91(phox)) activity and a significant (P < 0.05) elevation of reactive oxygen species within 12 h without coculture with IFN-gamma. This coincided with reduced survival of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium14028 phoP or stasis of S. enterica serovar Infantis phi(r). Fluorometric studies indicated that expression of IFN-gamma on infected J774.2 cells was not significantly (P > 0.05) elevated. However, studies with the virulent S. enterica serovar Typhimurium strains showed that a comparable level of control of bacterial numbers could only be achieved by coculture with IFN-gamma. This coincided with significant upregulation of IFN-gamma receptor alpha expression on the surface of J774.2 cells and was completely abolished by N-acetyl-L-cysteine captopril (an inhibitor of reactive oxygen species). Delay in reactive oxygen species induction due to a requirement for IFN-gamma and upregulation of IFN-gamma receptor alpha in macrophages infected with virulent salmonellae may result in greater dissemination of virulent salmonellae in host tissue.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) prevents killing of virulent and phoP mutant Salmonella typhimurium by inhibiting IFN-gamma stimulated NADPH oxidative pathways in murine macrophages.Cytokine. 2006 Nov;36(3-4):134-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2006.11.005. Epub 2006 Dec 15. Cytokine. 2006. PMID: 17174562
-
Stimulation of gp91 phagocytic oxidase and reactive oxygen species in neutrophils by an avirulent Salmonella enterica serovar infantis strain protects gnotobiotic piglets from lethal challenge with serovar Typhimurium strain F98 without inducing intestinal pathology.Infect Immun. 2005 Aug;73(8):4539-47. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.8.4539-4547.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16040965 Free PMC article.
-
The LysR-type transcriptional regulator Hrg counteracts phagocyte oxidative burst and imparts survival advantage to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Microbiology (Reading). 2008 Sep;154(Pt 9):2837-2846. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2008/017574-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2008. PMID: 18757817
-
Host-pathogen interaction in invasive Salmonellosis.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(10):e1002933. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002933. Epub 2012 Oct 4. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23055923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role of type I interferon-induced macrophage necroptosis during infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Cell Mol Immunol. 2013 Mar;10(2):99-100. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2012.68. Epub 2012 Dec 24. Cell Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23262973 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional modulation by VIP: a rational target against inflammatory disease.Clin Epigenetics. 2011 Aug;2(2):213-22. doi: 10.1007/s13148-011-0036-4. Epub 2011 May 18. Clin Epigenetics. 2011. PMID: 22704338 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma interferon enhances internalization and early nonoxidative killing of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium by human macrophages and modifies cytokine responses.Infect Immun. 2005 Jun;73(6):3445-52. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3445-3452.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15908373 Free PMC article.
-
The CFP-10/ESAT-6 complex of Mycobacterium tuberculosis potentiates the activation of murine macrophages involvement of IFN-gamma signaling.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2010 May;199(2):129-37. doi: 10.1007/s00430-010-0146-1. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20232079
-
Immunomodulation of innate immune responses by vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP): its therapeutic potential in inflammatory disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 Aug;157(2):225-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03956.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19604262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of murine dendritic cells and macrophages induced by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Immunology. 2005 Aug;115(4):462-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02180.x. Immunology. 2005. PMID: 16011515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buchmeier, N. A., C. J. Lipps, Y. Magdalene, Y. So, and F. Heffron. 1993. Recombinant deficient mutants of Salmonella are avirulent and sensitive to oxidative burst. Mol. Microbiol. 7:933-936. - PubMed
-
- Condino-Neto, A., and P. E. Newburger. 2000. Interferon-gamma improves splicing efficiency of CYBB gene transcripts in an interferon responsive variant of chronic granulomatous disease due to splice site consensus region mutation. Blood 95:3548-3554. - PubMed
-
- De Groote, M. A., U. A. Ochsner, M. U. Shiloh, C. Nathan, J. M. McCord, M. C. Dinauer, S. J. Libby, A. Vasquez-Torres, Y. Xu, and F. C. Fang. 1997. Periplasmic superoxide dismutase protects Salmonella from products of phagocyte NADPH-oxidase and nitric oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:13997-14001. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

